E-waste Management: Challenges and Solutions
E-waste, or discarded electrical and electronic equipment, poses significant environmental and health risks due to the toxic substances it contains. Proper e-waste management is crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure the sustainable disposal and recycling of electronic waste.
In this article, we will explore the challenges faced in e-waste management, as well as the solutions that can address these issues. From the exponential growth of e-waste generation to informal recycling practices and the lack of infrastructure and awareness, we will delve into the key obstacles and the strategies needed to overcome them.
Key Takeaways
- E-waste management is essential to prevent environmental and health risks associated with discarded electronic equipment.
- The challenges in e-waste management include skyrocketing e-waste generation, informal recycling practices, lack of infrastructure, and lack of awareness.
- Solutions to these challenges involve extended producer responsibility, investment in infrastructure, consumer education, policy and regulation, collaboration, certifications and standards, and research and technological innovations.
- Collective action and innovative solutions are needed to tackle the e-waste crisis and promote sustainable e-waste management.
- Proper e-waste management can protect the environment, reduce health hazards, and create a cleaner and greener future.
Skyrocketing E-Waste Generation
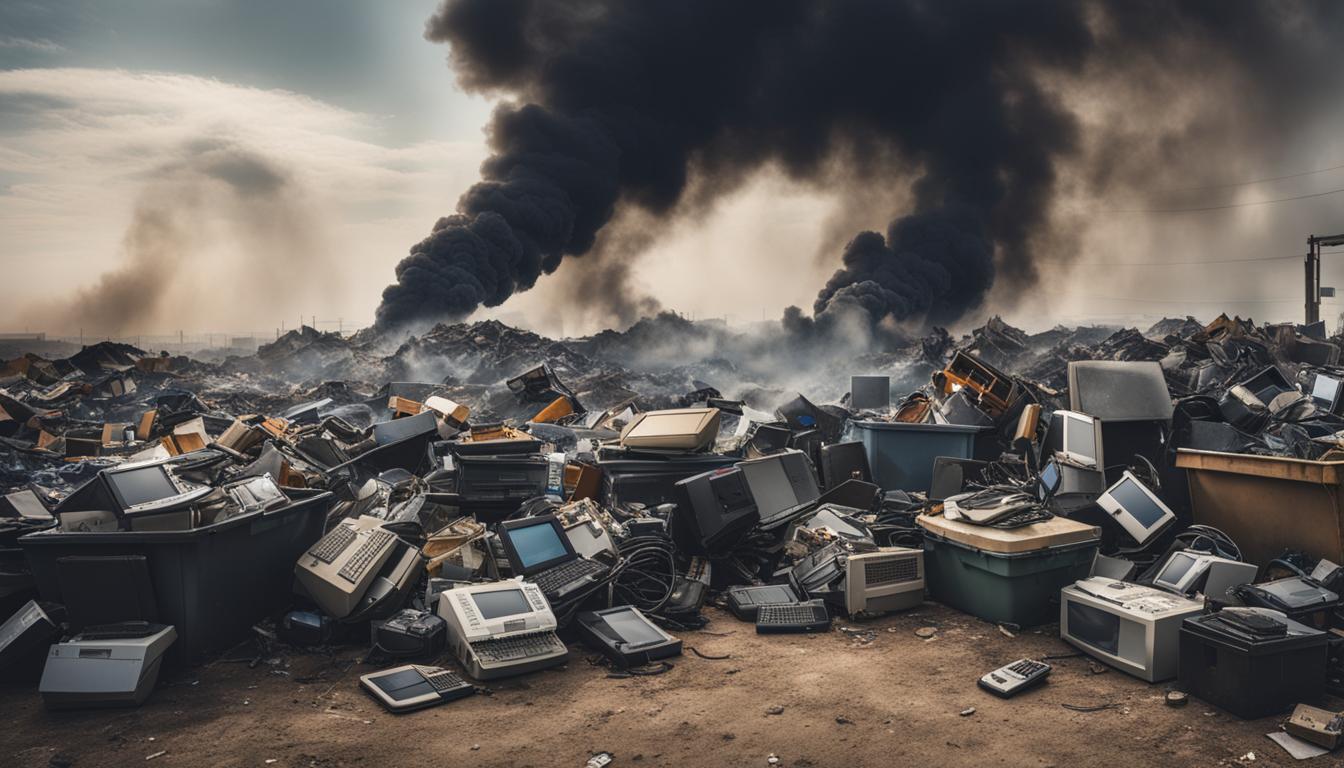
E-waste generation is reaching alarming levels due to the constant introduction of new electronic products and the frequent upgrading of devices. This rapid growth has resulted in a mounting volume of electronic waste that poses significant challenges in terms of disposal and recycling. Without proper management, this skyrocketing e-waste generation can lead to severe environmental and health hazards.
The increasing demand for electronic gadgets and the short lifespan of many devices contribute to the exponential growth of e-waste. Consumers are constantly enticed by the latest models, leading to a higher turnover of electronic devices and a larger accumulation of discarded products. These devices contain hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can contaminate soil, water, and air if not handled properly.
To address the issue of skyrocketing e-waste generation, it is essential to promote responsible consumption and sustainable product design. Encouraging consumers to choose products with longer lifespans and supporting manufacturers in creating more durable and repairable devices can help reduce the amount of electronic waste generated. Additionally, implementing effective take-back programs and establishing convenient collection points for electronic recycling can encourage individuals to dispose of their old devices responsibly.
The Impact of Skyrocketing E-Waste Generation
The repercussions of skyrocketing e-waste generation are far-reaching. Improper disposal practices, such as landfilling or incineration, can release toxic substances into the environment, endangering both ecosystems and human health. Moreover, the extraction of raw materials from electronic waste in informal recycling practices often involves hazardous techniques that further contribute to environmental pollution and worker exploitation.
It is crucial to recognize the urgency of addressing this issue and to implement comprehensive e-waste management strategies. By prioritizing responsible consumption, designing eco-friendly products, and establishing efficient recycling systems, we can minimize the environmental impact of e-waste and work towards a more sustainable future.
| Effects of Skyrocketing E-Waste Generation | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Pollution of soil, water, and air | Encouraging responsible consumption |
| Health hazards due to toxic substances | Supporting durable and repairable product design |
| Worker exploitation in informal recycling | Implementing effective take-back programs |
Table: Effects of Skyrocketing E-Waste Generation and Corresponding Solutions
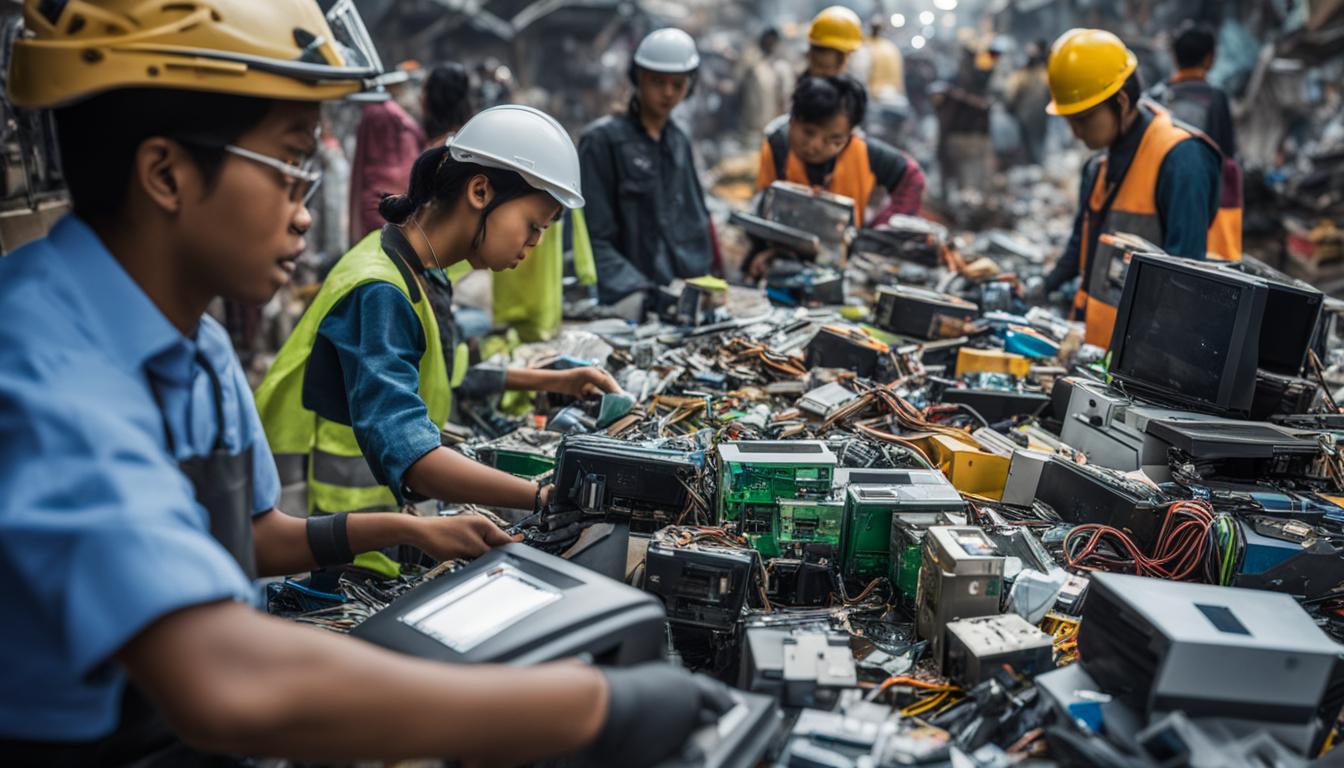
Informal Recycling Practices
One of the key challenges in e-waste management is the prevalence of informal recycling practices. In many regions, e-waste is managed through these informal channels, which often involve hazardous and unsafe methods of handling electronic waste. This not only poses a significant risk to the environment but also compromises the health and safety of those involved in the recycling process.
Informal recyclers often resort to dangerous techniques such as burning or acid leaching to extract valuable materials from electronic waste. These methods release toxic fumes into the air and leave behind harmful residues that can contaminate soil and water sources. Additionally, informal recycling practices occur in unregulated environments, further exacerbating the risk and impact on the ecosystem.
To address this issue, it is essential to formalize and regulate the e-waste recycling process. By implementing strict standards and guidelines, authorities can ensure that recycling facilities adhere to proper practices that prioritize the health and safety of workers and minimize environmental harm. This would involve providing training and guidance to recyclers, promoting the use of safer methods, and enforcing regulations to prevent the unauthorized operation of informal recycling facilities.
Furthermore, raising awareness among the general public about the dangers of informal recycling practices is crucial. Educating individuals about the importance of responsible e-waste management and the availability of formal recycling options can encourage them to make informed choices and dispose of their electronic devices properly. Public campaigns, community outreach programs, and educational initiatives can play a vital role in spreading awareness and promoting responsible e-waste recycling.
| Impact of Informal Recycling Practices | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Environmental | Pollution of air, water, and soil due to toxic fume emissions and leaching of hazardous substances |
| Health | Exposure to dangerous chemicals and heavy metals, leading to respiratory problems, neurological disorders, and other serious health issues |
| Social | Exploitation of workers, often in unsafe working conditions, and the perpetuation of poverty in informal recycling communities |
By addressing informal recycling practices and promoting formalized systems, we can mitigate the environmental and health risks associated with e-waste management. It requires a collaborative effort involving governments, regulatory bodies, recycling industries, and the public to ensure the sustainable disposal and recycling of electronic waste.
Lack of Infrastructure
The effective management of e-waste requires a robust infrastructure that encompasses the entire lifecycle of electronic products, from collection to recycling and disposal. However, one of the significant challenges in e-waste management is the lack of adequate infrastructure to handle the growing volume of electronic waste. This lack of infrastructure hinders the proper handling and processing of e-waste, leading to environmental and health risks.
Infrastructure gaps exist in various aspects of e-waste management. Firstly, there is a shortage of collection points and facilities for the proper disposal of electronic devices. Many consumers find it inconvenient to access drop-off locations or recycling centers, resulting in improper disposal methods such as throwing electronic waste in regular trash bins. This leads to e-waste ending up in landfills, where harmful chemicals and substances can seep into the soil and water sources.
Moreover, the shortage of processing and recycling facilities further exacerbates the problem. E-waste contains valuable materials that can be recovered and reused, but without the necessary infrastructure, these materials often go to waste. To address this issue, investment in the development and improvement of e-waste recycling infrastructure is crucial. Governments and organizations need to allocate resources for the establishment of state-of-the-art recycling plants that can safely handle and extract valuable components from electronic waste.
E-waste Infrastructure Comparison:
| Country | Collection Points | Recycling Facilities | Processing Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Country A | Only 100 | 5 | 5,000 tons/year |
| Country B | 500 | 10 | 10,000 tons/year |
| Country C | 1,000 | 20 | 20,000 tons/year |
Without proper infrastructure, the management of e-waste becomes challenging, and the risks associated with e-waste disposal persist. Therefore, governments, policymakers, and industry stakeholders need to prioritize the development and improvement of e-waste recycling infrastructure to ensure the safe and efficient handling of electronic waste.
Lack of Awareness
A significant obstacle to addressing the e-waste crisis is a lack of awareness among consumers, businesses, and policymakers. Many people are uninformed about the proper disposal and recycling options for electronic devices, leading to improper e-waste management. Without sufficient knowledge, individuals may discard their electronic waste in regular trash bins or donate it to charity organizations that may not have the means to handle e-waste appropriately.
Increasing consumer education and awareness is key to tackling this issue. Public campaigns can play a crucial role in informing the public about the environmental and health risks associated with improper e-waste disposal. These campaigns should provide clear and accessible information on the importance of recycling electronic devices and the various disposal options available, such as dedicated e-waste recycling centers or manufacturer take-back programs.
Government and non-profit organizations should collaborate to develop educational materials and initiatives targeting consumers, businesses, and policymakers. These materials should be readily available through online platforms, community centers, and public spaces to ensure broad dissemination. By empowering individuals with knowledge about responsible e-waste management, we can encourage them to make informed choices and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
The challenges in e-waste management require collective action and innovative solutions. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) ensures that manufacturers take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, including proper disposal and recycling. Investment in infrastructure, such as collection centers and recycling facilities, is vital to ensure the safe handling and processing of electronic waste.
Consumer education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting responsible e-waste management. By providing information on recycling options and the environmental impacts of improper disposal, individuals can make informed choices and contribute to sustainable solutions. Additionally, policymakers need to implement and enforce policies and regulations that facilitate proper e-waste disposal and incentivize recycling.
Collaboration between governments, businesses, and NGOs is essential to address the e-waste crisis comprehensively. This collaboration can involve sharing best practices, supporting research and development, and establishing certifications and standards for responsible electronic waste recycling. Technological innovations, such as improved recycling processes and the development of eco-friendly materials, will also contribute to sustainable e-waste management.
By implementing these solutions, we can make significant progress in managing e-waste effectively. Sustainable e-waste management not only protects the environment but also helps conserve valuable resources and promotes a cleaner and greener future for generations to come.
FAQ
What is e-waste?
E-waste refers to discarded electrical and electronic equipment, including devices like smartphones, laptops, TVs, and appliances, that are no longer functional or are obsolete.
Why is e-waste a concern?
E-waste poses significant environmental and health risks due to the toxic substances it contains, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium. Improper disposal and recycling practices can lead to environmental pollution and harm to human health.
What are the challenges in e-waste management?
The challenges in e-waste management include the exponential growth of e-waste generation, informal recycling practices, lack of infrastructure, lack of awareness, presence of toxic components, and the need for global cooperation.
How can e-waste generation be controlled?
E-waste generation can be controlled through strategies such as Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR). EPR holds manufacturers accountable for the entire life cycle of their products, including their proper disposal and recycling.
What are informal recycling practices?
Informal recycling practices refer to the unregulated and often unsafe methods used by individuals or small-scale operations to extract valuable materials from e-waste. These practices can lead to environmental pollution and health hazards.
How can the lack of infrastructure be addressed?
The lack of infrastructure in e-waste management can be addressed through investments in the development and improvement of collection, processing, and recycling facilities. This includes establishing dedicated e-waste recycling centers and promoting the establishment of recycling infrastructure.
How can consumer awareness be increased?
Consumer awareness can be increased through public campaigns and education programs that provide information on proper e-waste disposal and recycling options. This can empower individuals to make responsible choices and promote sustainable e-waste management.
What are the solutions to the e-waste crisis?
Solutions to the e-waste crisis include Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), investment in infrastructure, consumer education and awareness, policy and regulation, collaboration, establishment of certifications and standards, and research and technological innovations.
How can I contribute to e-waste management?
You can contribute to e-waste management by responsibly disposing of your electronic devices through proper recycling channels. Educate yourself about e-waste recycling options in your area and choose certified recycling centers to ensure your devices are recycled safely and sustainably.