The Rise of Repair Cafes and Their Role in IT Sustainability
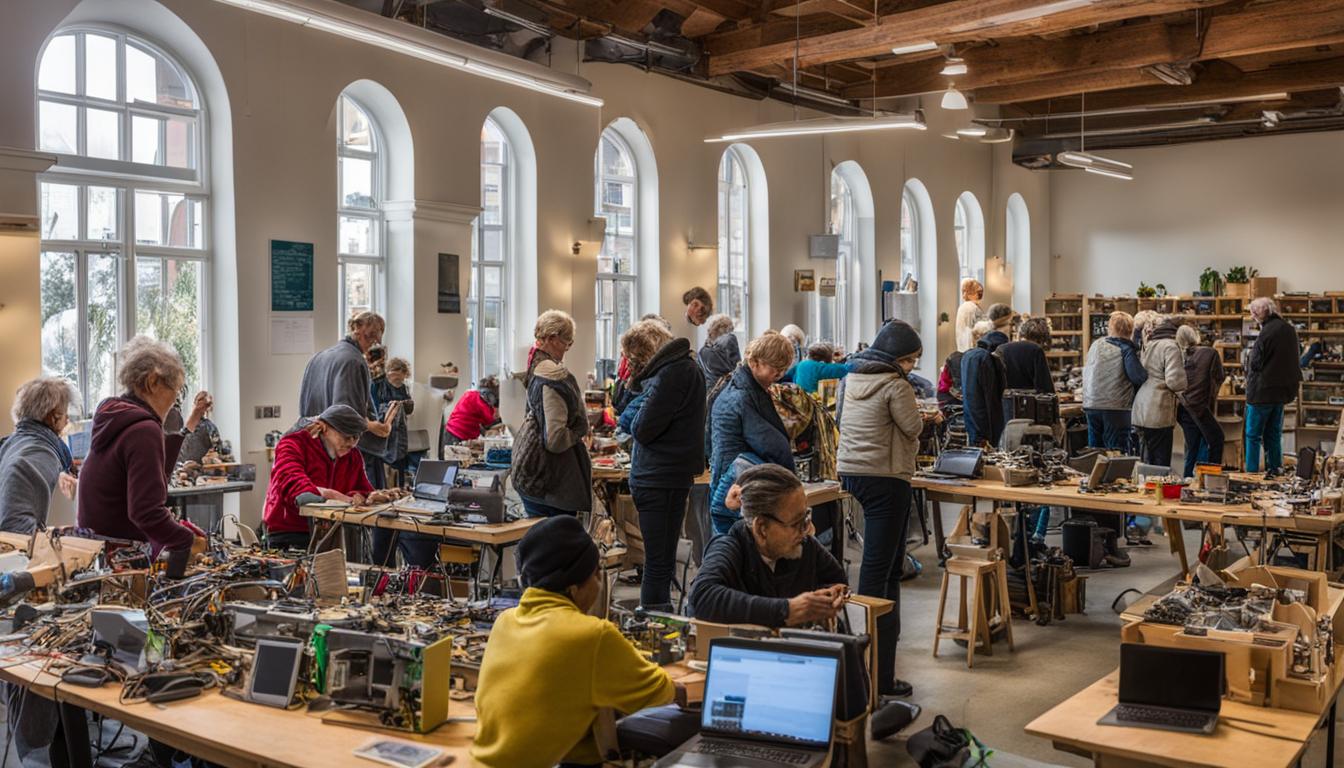
Repairing broken and faulty products is crucial for achieving a circular economy and reducing waste. Repairing items uses less energy than producing new ones and is more environmentally friendly. Repair cafes, as a form of non-commercial repair, have gained popularity globally, with over 2,000 repair cafes in 37 countries. These cafes provide a platform for individuals to repair small items themselves or with the assistance of volunteers, promoting sustainable repair practices and fostering a sense of community.
Key Takeaways
- Repair cafes contribute to IT sustainability by promoting repair over replacement.
- They provide a platform for individuals to repair items themselves or with volunteer assistance.
- Repair cafes foster a sense of community and promote sustainable repair practices.
- By repairing items, repair cafes reduce waste and conserve resources.
- Repair cafes have gained global popularity, with over 2,000 cafes in 37 countries.
Benefits of Repair Cafes for Sustainable Living
Repair cafes play a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability and sustainable living. By providing a space for individuals to repair broken or faulty items, these cafes contribute to reducing electronic waste and conserving natural resources. Repairing items instead of discarding them helps to minimize the carbon emissions and energy consumption associated with manufacturing new products. This environmentally friendly approach aligns with the principles of the circular economy, where the aim is to extend the lifespan of products and reduce waste.
One of the key benefits of repair cafes is that they empower individuals to gain repair skills and knowledge. Through workshops and guidance from volunteers, people can learn how to fix their belongings and become more self-sufficient in addressing minor repairs. This reduces their reliance on professional repair services, which can be costly and may involve replacing parts unnecessarily. By equipping individuals with repair skills, repair cafes not only promote sustainable repair practices but also encourage a shift towards a more resourceful and self-reliant society.
Moreover, repair cafes foster a sense of community and social cohesion. These spaces bring together people from different backgrounds and age groups who share a common interest in sustainability and environmental consciousness. By creating opportunities for individuals to interact, collaborate, and share knowledge, repair cafes build connections and strengthen relationships within the community. These social benefits contribute to a more inclusive and collaborative society that values sustainable practices and actively works towards reducing waste and promoting environmental well-being.
Table: Environmental Impact of Repair Cafes
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduction of electronic waste | By repairing items instead of discarding them, repair cafes contribute to the reduction of electronic waste, which is a significant environmental concern. |
| Conservation of resources | Repair cafes help conserve natural resources by extending the lifespan of products and reducing the demand for new production. |
| Carbon footprint reduction | By minimizing the need for new products, repair cafes contribute to reducing carbon emissions associated with manufacturing and transportation. |
| Promotion of sustainable consumption | Repair cafes raise awareness about the environmental impact of consumerism and encourage more sustainable patterns of consumption. |
The Impact of Repair Cafes on the Circular Economy
Repair cafes play a significant role in promoting the principles of the circular economy. By extending the lifespan of products through repair, these cafes contribute to stock optimization and waste prevention. Repairing items reduces the need for new production, thus reducing resource consumption and minimizing waste. This aligns with the concept of slowing resource loops and transitioning to a more sustainable economy.
Not only do repair cafes prevent items from ending up in landfills, but they also promote the repairability and durability of products. By emphasizing the importance of repairing rather than replacing, these cafes encourage a shift towards sustainable technology. This mindset challenges the prevailing culture of planned obsolescence, where products are intentionally designed to have a limited lifespan or be difficult to repair.
Furthermore, repair cafes can collect and share crucial data that can inform product design and policies. This data can help manufacturers improve the reparability of their products, ultimately supporting the transition to a circular economy. By working together with stakeholders, repair cafes contribute to the creation of a more sustainable future by promoting mindful consumption and responsible production practices.
| Impact of Repair Cafes on the Circular Economy | |
|---|---|
| Contributing to stock optimization and waste prevention | ✓ |
| Promoting repairability and durability of products | ✓ |
| Challenging planned obsolescence | ✓ |
| Collecting and sharing data for product design and policies | ✓ |
The Growth and Spread of Repair Cafes
The repair cafe movement has gained significant momentum since the establishment of the first repair cafe in Amsterdam in 2009. It has now spread to over 35 countries, with thousands of repair cafes offering their services to individuals seeking to fix their broken or faulty items. Repair cafes have become a symbol of the grass-roots effort to reduce waste and change the culture of disposable consumer goods.
What sets repair cafes apart is their dedication to advocating for legislation that supports the right to repair. This movement is pushing for manufacturers to design products that are more repairable and durable, reducing the need for constant replacement. By promoting the right to repair, repair cafes aim to tackle the issue of planned obsolescence, where products are intentionally designed to have a limited lifespan or be difficult to repair. Through their collective efforts, repair cafes are reshaping the consumer landscape and encouraging a more sustainable approach to consumption.
Repair cafes are driven by the belief that repair should be accessible to all, regardless of financial constraints or lack of technical skills. These cafes provide a supportive environment where individuals can learn to repair their belongings or receive assistance from skilled volunteers. By empowering individuals to take control of their repair needs, repair cafes foster a sense of self-sufficiency and community. They bring people together, transcending social and economic barriers, to create a more inclusive and collaborative society.
Repair cafes are not just places where items are fixed; they are spaces for community building, knowledge sharing, and education. They embody the spirit of grass-roots activism, inspiring individuals to take action towards a more sustainable future. Repair cafes are a testament to the power of collective effort and the potential for positive change.
The Impact of Repair CafesTable 1
| Country | Number of Repair Cafes | Year Established |
|---|---|---|
| Netherlands | 600+ | 2009 |
| Germany | 500+ | 2010 |
| France | 250+ | 2013 |
| United Kingdom | 150+ | 2011 |
| United States | 100+ | 2013 |
| Canada | 100+ | 2015 |
Table 1 showcases the impact of repair cafes by highlighting the number of cafes established in different countries and their respective establishment years. The Netherlands, being the birthplace of the repair cafe movement, takes the lead with over 600 cafes. Germany closely follows with more than 500 cafes. The movement has also gained significant traction in France, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Canada.
The Environmental Impact of Repair Cafes
Repair cafes have emerged as a powerful solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, carbon footprints, and electronic waste. By extending the lifespan of products, these cafes prevent the unnecessary disposal of items and contribute to a more sustainable future. The environmental impact of repair cafes goes beyond individual repair actions – it has the potential to create a ripple effect that positively influences our planet.
When we repair and reuse items instead of buying new ones, we significantly reduce the demand for new production. This reduction in manufacturing translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions. For example, repairing a mobile phone instead of buying a new one can save approximately 16 kilograms of CO2 emissions – equivalent to the carbon footprint of charging a smartphone for two years. Repair cafes, like The Restart Project in London, have already prevented thousands of kilograms of CO2 emissions through their repair initiatives.
Additionally, repair cafes play a critical role in tackling the growing challenge of electronic waste. Electronic devices contain valuable resources like metals and plastics, but improper disposal leads to e-waste and pollution. By repairing electronic devices, repair cafes prevent the premature disposal of these items, reducing the need for extraction of raw materials and minimizing waste. This not only conserves resources but also reduces the energy-intensive process of recycling or remanufacturing electronic products.
| Environmental Impact of Repair Cafes | Data |
|---|---|
| CO2 Emissions Prevented by Repairing Mobile Phones | Thousands of kilograms |
| E-waste Diverted from Landfills | Significant reduction |
| Resources Conserved through Repair | Raw materials, energy |
Repair cafes not only address environmental issues but also raise awareness about the impact of consumerism on our planet. By providing repair services and promoting sustainable patterns of consumption, these cafes encourage individuals to make conscious choices and consider the environmental consequences of their purchasing decisions. They inspire a shift away from a throwaway culture towards a more circular economy, where products are repaired and reused, reducing waste and conserving resources.

The Impact of Repair Cafes: A Quote from Sustainable Living Expert, Jane Smith
“Repair cafes serve as a fundamental pillar for achieving sustainability in our society. By extending the lifespan of products and reducing waste, these cafes demonstrate the power of repair in mitigating our environmental impact. They not only encourage individuals to rethink their consumption patterns but also foster a sense of community engagement and empowerment. Repair cafes offer tangible solutions that enable us to live more sustainably and create a better future for generations to come.”
The Social Benefits of Repair Cafes
Alongside their significant role in promoting sustainability, repair cafes offer a range of social benefits that contribute to community building and knowledge sharing. These cafes act as hubs for individuals of all ages and backgrounds to come together, fostering a sense of community and connection.
“Repair cafes build bridges between people that might not otherwise meet in their local communities.”
At repair cafes, volunteers and participants have the opportunity to share their skills and knowledge, creating an environment of collaboration and education. This exchange of expertise empowers individuals to become more confident in repairing their belongings, reducing reliance on professional repair services and promoting a do-it-yourself mentality.
Furthermore, repair cafes play a vital role in preserving traditional repair practices, particularly among older citizens who possess valuable repair expertise. By offering opportunities for older generations to share their skills and wisdom, repair cafes ensure that these knowledge assets are passed down to younger generations, preserving valuable insights and promoting intergenerational learning.
Community Building and Empowerment
Repair cafes go beyond simply fixing broken items; they actively promote community building and social empowerment. Through face-to-face interactions and shared experiences, repair cafes create spaces where people can connect, build relationships, and foster a sense of belonging.
- Repair cafes bring together individuals from diverse backgrounds, breaking down barriers and promoting social cohesion.
- They provide a supportive environment where individuals can learn from each other and gain confidence in their repair abilities.
- Participants leave repair cafes with not only repaired items but also new skills, knowledge, and a sense of empowerment.
In an increasingly disconnected world, repair cafes offer a haven for human connection and community spirit. They serve as catalysts for building stronger, more resilient communities that are actively engaged in sustainable practices and collective problem-solving.
| Benefits of Repair Cafes | Sustainable Living | Community Building | Empowerment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Opportunity for knowledge sharing | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Encourages collaboration and education | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Promotes intergenerational learning | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Fosters a sense of community and connection | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Challenges and Future Considerations for Repair Cafes
Repair cafes face various challenges in their mission to promote sustainable repair and combat planned obsolescence. One significant obstacle is the practice of planned obsolescence, where products are intentionally designed to have a limited lifespan or be difficult to repair. This practice forces consumers to constantly replace their belongings, contributing to the cycle of waste and consumption. To address this challenge, repair cafes advocate for better product design and the right to repair legislation, which would require manufacturers to create products that are more repairable and durable.
Changing consumer behavior and attitudes towards repair is also essential for the success of repair cafes. Many individuals are accustomed to the convenience of disposable consumer goods, and the concept of repair may be unfamiliar or undervalued. Financial constraints can also be a barrier to seeking repair options, as professional repair services can be costly. Additionally, lack of trust in repair services and limited knowledge or skills in repair can further discourage individuals from pursuing repair options.
To overcome these challenges, collaborative efforts are needed. Advocacy for better product design and the right to repair legislation can help create a more repair-friendly market. Consumer education campaigns can raise awareness about the benefits of repair and empower individuals to make more sustainable choices. Increasing the accessibility of repair services, such as through the expansion of repair cafe networks or the development of online repair resources, can also help overcome barriers to repair.
| Challenges | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Planned obsolescence | Advocacy for better product design |
| Consumer behavior and attitudes | Consumer education campaigns |
| Financial constraints | Increased accessibility of repair services |
| Lack of trust and limited knowledge/skills | Expansion of repair cafe networks |
Repair cafes face challenges in their mission to promote sustainable repair. Changing consumer behavior and attitudes towards repair, financial constraints, lack of trust in repair services, and limited knowledge or skills in repair can be barriers. Overcoming these challenges requires collaborative efforts, including advocacy for better product design, consumer education, and improved accessibility to repair services.
Conclusion
Repair cafes have emerged as important contributors to IT sustainability and sustainable living. By promoting repair and extending the lifespan of products, these cafes play a significant role in reducing waste, conserving resources, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Repair cafes not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also foster a sense of community and empowerment through knowledge sharing and social connections.
Despite challenges, such as planned obsolescence and consumer behavior, repair cafes continue to grow and have the potential to make a significant impact on creating a more sustainable future. These cafes not only help in reducing electronic waste but also encourage individuals to gain repair skills and knowledge, empowering them to fix their belongings rather than relying on professional repair services.
Moreover, repair cafes align with the principles of the circular economy by extending the lifespan of products and minimizing waste. They also promote the concept of slowing resource loops through product life extension. Repair cafes can contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprints by preventing the unnecessary disposal of items, especially electronic devices, thus helping to combat climate change.
In conclusion, repair cafes are not just about repairing broken items; they are about creating a sustainable and inclusive society. These cafes provide a platform for individuals to repair small items themselves or with the assistance of volunteers, promoting sustainable repair practices and fostering a sense of community. By embracing repair cafes and supporting their growth, we can collectively work towards a more sustainable future.
FAQ
What is a repair cafe?
A repair cafe is a non-commercial establishment where individuals can repair small items themselves or with the assistance of volunteers. It provides a platform for promoting sustainable repair practices and fostering a sense of community.
Why are repair cafes important for IT sustainability?
Repair cafes play a vital role in reducing electronic waste and conserving resources. By extending the lifespan of products, these cafes contribute to IT sustainability and help reduce carbon emissions.
How many repair cafes are there globally?
There are over 2,000 repair cafes in 37 countries, and the movement continues to grow.
What are the social benefits of repair cafes?
Repair cafes build communities by bringing together volunteers and individuals of all ages and backgrounds. They promote knowledge sharing, skill development, and social connections.
How do repair cafes contribute to the circular economy?
Repair cafes align with the principles of the circular economy by extending the lifespan of products and minimizing waste. They promote stock optimization, waste prevention, and the concept of slowing resource loops.
What challenges do repair cafes face?
Repair cafes face challenges such as planned obsolescence, consumer behavior, and financial constraints. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration, advocacy, and consumer education.