The Global Landscape of E-waste Management
Introduction: Navigating the Complexities of the Global Landscape of E-waste Management
The Global Landscape of E-waste Management is a topic of increasing importance as the world grapples with the challenges of electronic waste. With the rapid advancement of technology, electronic devices have become an integral part of our daily lives. However, this convenience comes at a cost—millions of tons of e-waste are generated each year, posing significant environmental and health risks.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the global landscape of e-waste management, exploring the current state of e-waste disposal, recycling practices, and the role of governments and organizations in shaping policies. We’ll delve into the complexities of managing e-waste on a global scale, from the challenges of regulatory compliance to the opportunities for sustainable practices.
Current State of E-waste Disposal: A Global Perspective
Understanding the current state of e-waste disposal on a global scale is crucial for grasping the complexities of the Global Landscape of E-waste Management. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented rate, the generation of e-waste has reached alarming levels. In 2020 alone, the world produced approximately 53.6 million metric tons of electronic waste, a figure that is expected to grow annually.
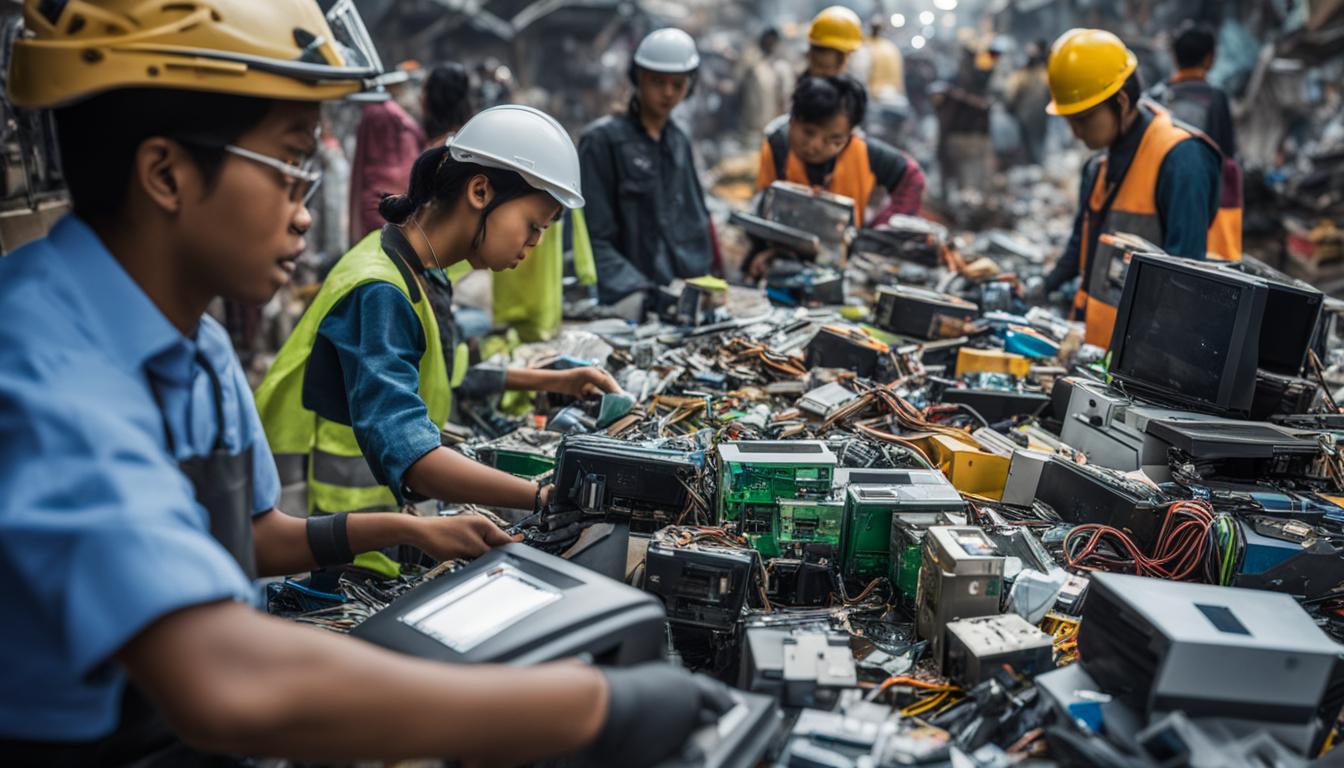
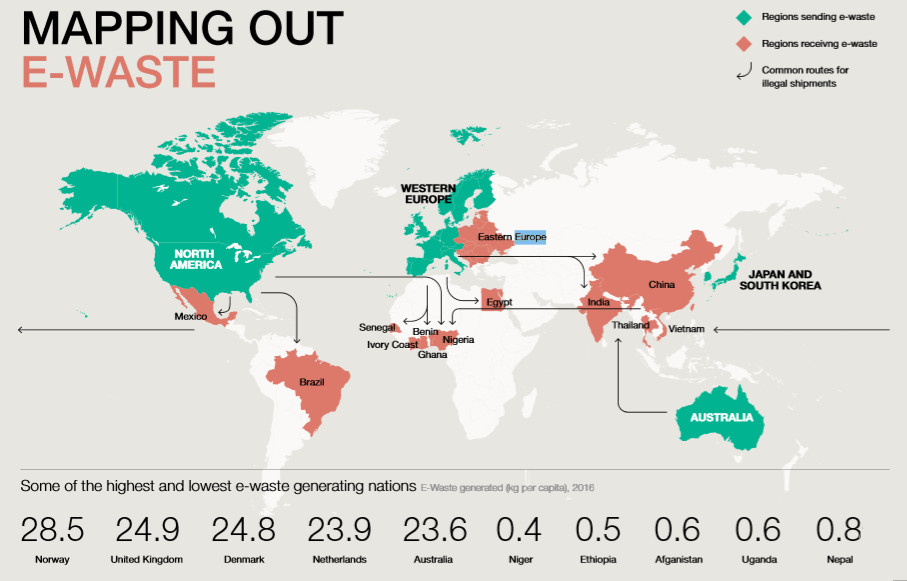
E-waste Hotspots: Regions with High E-waste Generation
Certain regions, particularly in developed countries, are significant contributors to the global e-waste problem. The United States, China, and European countries are among the top generators of electronic waste, often exporting their e-waste to developing nations, thereby exacerbating the issue.
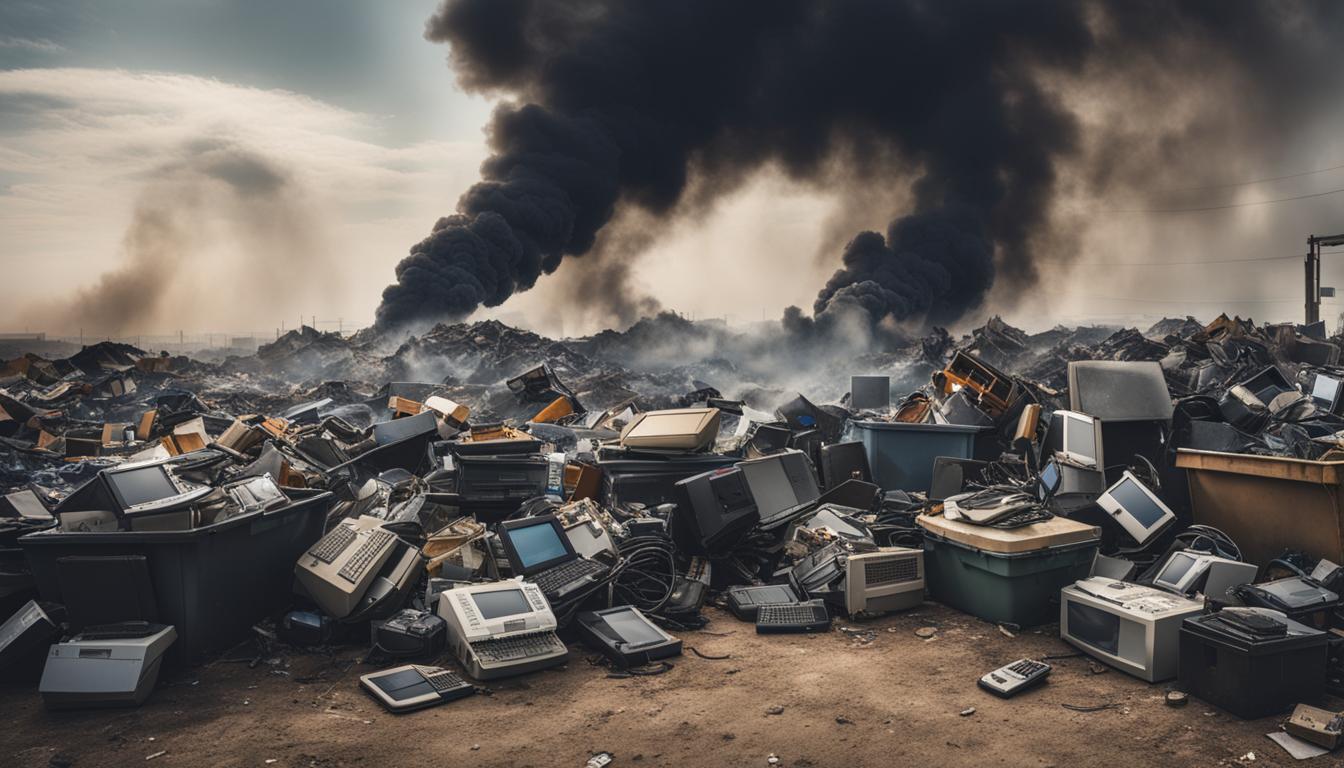
The Environmental Impact of Improper E-waste Disposal
The environmental consequences of improper e-waste disposal are severe, including soil and water contamination from hazardous materials like lead and mercury. This not only poses risks to human health but also has a long-lasting impact on ecosystems.
The Role of Landfills in E-waste Management
While landfills have been the traditional method for disposing of waste, including electronics, they are increasingly viewed as unsustainable and harmful. The challenges and limitations of using landfills for e-waste management are becoming more apparent, leading to a push for more sustainable alternatives.
By examining the current state of e-waste disposal, we can better understand the urgent need for effective e-waste management strategies on a global scale. This sets the stage for discussing the role of recycling practices, government policies, and sustainable initiatives in shaping the future of e-waste management.
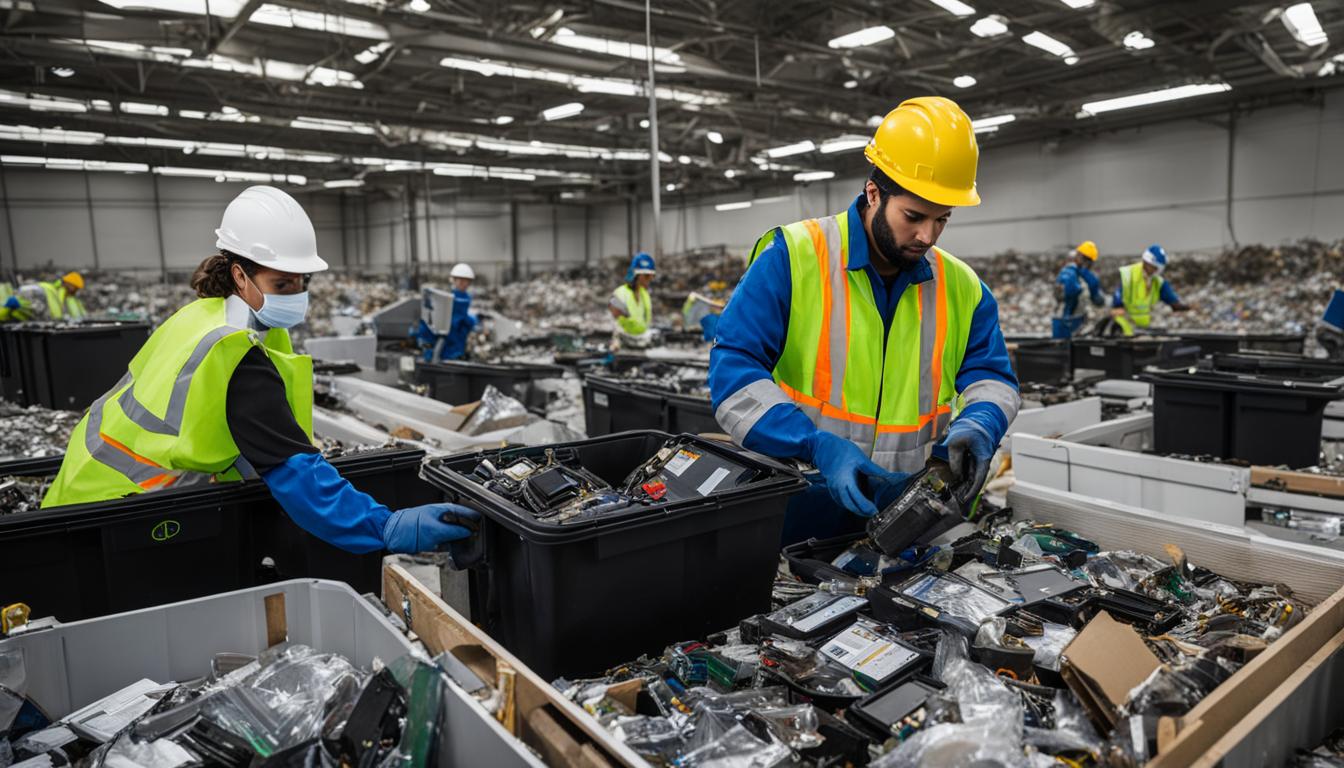
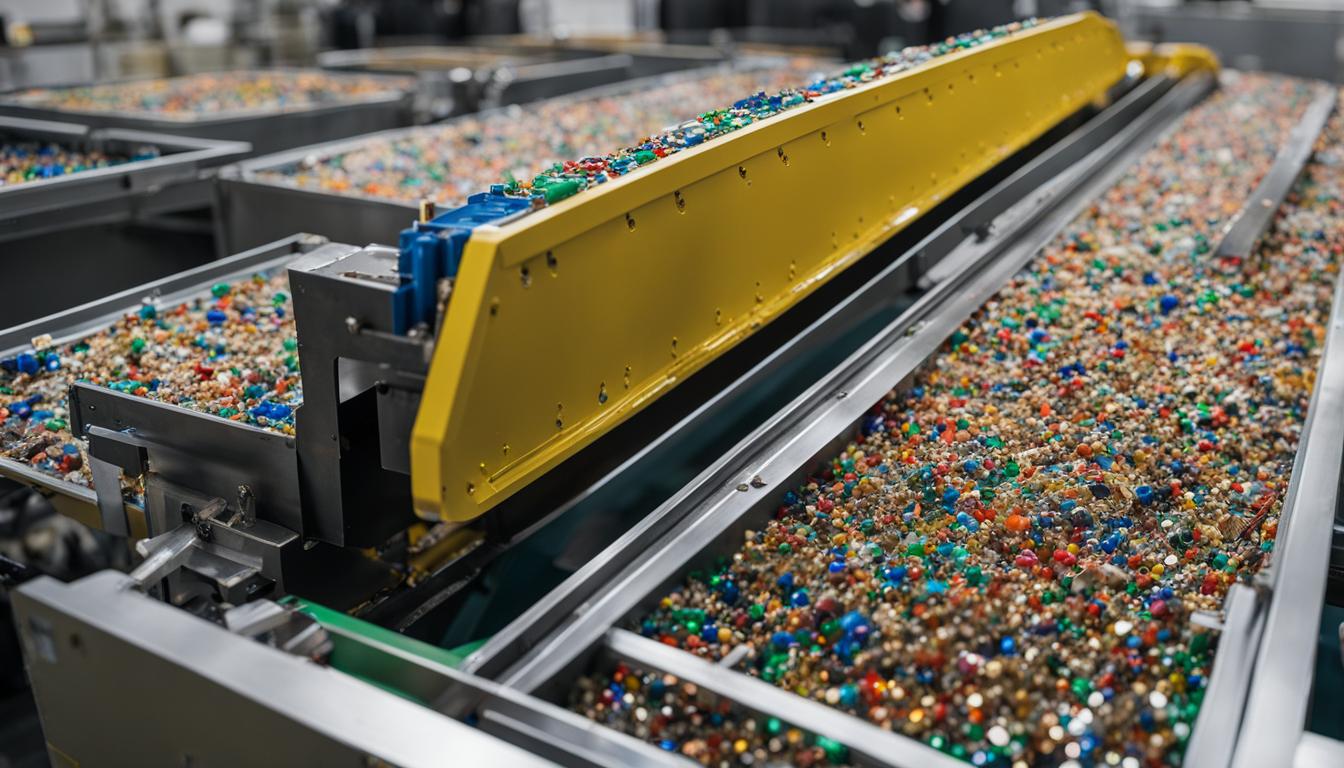
Recycling Practices and Innovations: A Global Overview
As we navigate the Global Landscape of E-waste Management, it becomes evident that recycling practices play a pivotal role in mitigating the environmental impact of e-waste. However, the sad reality is that a significant portion of e-waste ends up in landfills or is improperly disposed of, leading to environmental degradation.
Traditional vs. Modern Recycling Methods
Traditionally, e-waste was often melted down to extract valuable metals, a process that released harmful toxins into the environment. Modern recycling methods are increasingly focusing on sustainable e-waste management practices, which include advanced techniques for material recovery and safe disposal.
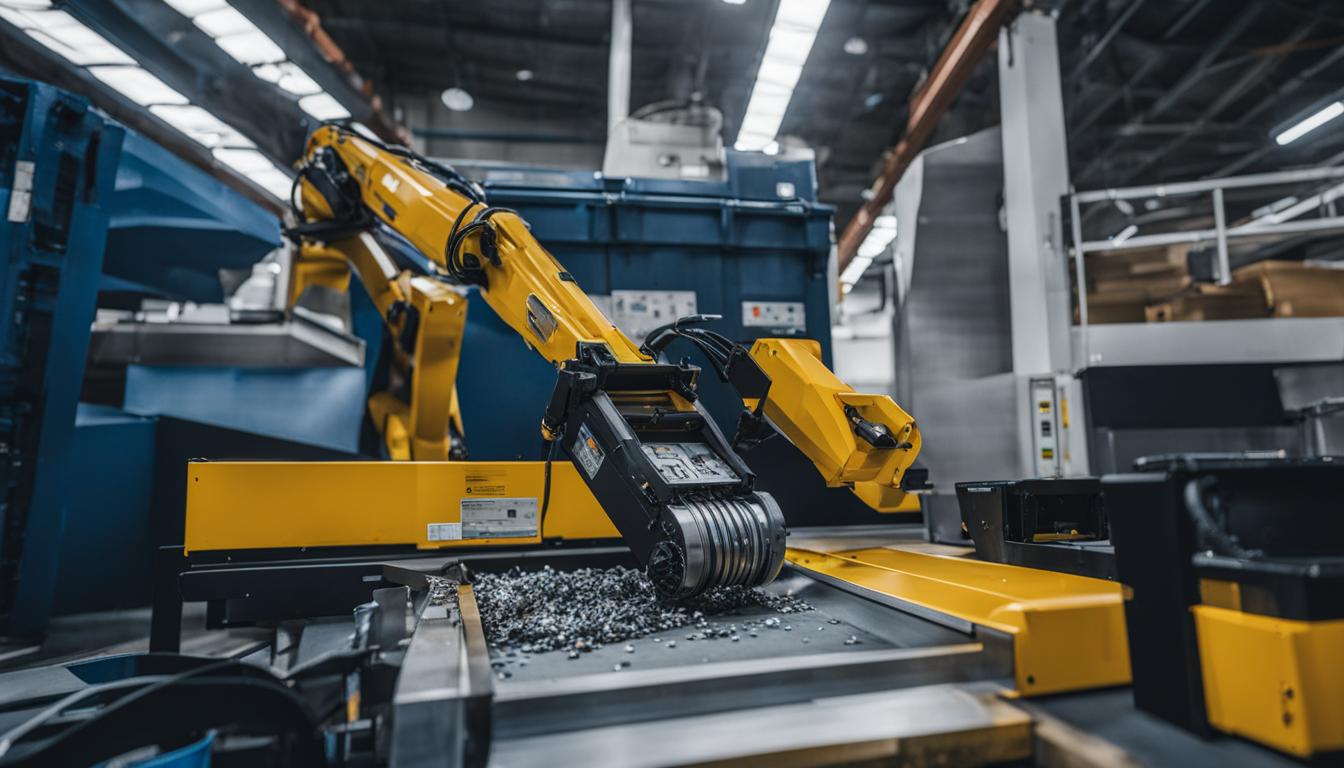
Innovations in E-waste Recycling
Technological advancements are driving innovations in e-waste recycling. From automated sorting systems to eco-friendly extraction methods, these innovations aim to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of e-waste management.
The Role of Private and Public Sectors
Both the private and public sectors have a role to play in shaping the future of e-waste management. Companies are investing in innovative e-waste recycling technologies, while governments are implementing policies to regulate e-waste disposal and encourage recycling.
According to a recent report, it is anticipated that by 2023, over 347 million metric tonnes of electronic garbage will be created globally that will not be recycled. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for effective e-waste management strategies.
By understanding the current recycling practices and innovations, we can better appreciate the complexities and opportunities in the Global Landscape of E-waste Management. This sets the stage for discussing the role of government policies and international collaborations in the next section.
Government Policies and International Collaborations: Shaping the Future of E-waste Management
Navigating the Global Landscape of E-waste Management is a complex endeavor that requires concerted efforts from various stakeholders, including governments and international organizations. This section will explore how these entities are shaping the future of e-waste management.
Government Regulations: A Double-Edged Sword
While government regulations are essential for ensuring responsible e-waste management, they can also pose challenges. For instance, stringent regulations can sometimes hinder the adoption of innovative e-waste recycling technologies. Therefore, a balanced approach is needed to encourage both compliance and innovation.
International Collaborations: A Step Towards Global Solutions
The issue of e-waste transcends national boundaries, making international collaborations crucial for effective e-waste management. Various global initiatives aim to standardize e-waste management practices and promote sustainable e-waste management on a global scale.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Several countries have successfully implemented e-waste management strategies, serving as models for others. For example, countries like Sweden and Japan have high e-waste recycling rates, thanks to effective government policies and public awareness campaigns.
By examining the role of government policies and international collaborations, we gain valuable insights into the potential for shaping a more sustainable and effective Global Landscape of E-waste Management. This sets the stage for our final section, which will discuss the challenges and future prospects of e-waste management.
Challenges and Future Prospects: Navigating the Road Ahead in E-waste Management
As we’ve delved into the complexities of the Global Landscape of E-waste Management, it’s evident that the journey ahead is fraught with challenges. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration among stakeholders.
Technological Limitations: The Need for Innovation
While there have been significant advancements in e-waste recycling technologies, limitations still exist. For instance, the extraction of certain rare metals from e-waste remains a complex and costly process. These technological limitations necessitate further research and development to unlock the full potential of sustainable e-waste management practices.
Regulatory Hurdles: The Complexity of Global Regulations
The regulatory landscape for e-waste management is a complex web of local, national, and international laws. This complexity often leads to challenges in implementing effective e-waste management strategies on a global scale. Regulatory alignment and international collaborations could offer solutions to these challenges.
Public Awareness: The Missing Link
Public awareness is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of e-waste management. The lack of knowledge about the environmental and health risks associated with improper e-waste disposal hampers effective management. Educational campaigns, both online and offline, are crucial for raising awareness and encouraging responsible behavior.
Future Prospects: Towards a Sustainable Future
Despite the challenges, there are promising signs for the future of e-waste management. Countries like Sweden and Japan have successfully implemented e-waste management strategies, serving as models for other nations. Their success stories, as highlighted in this comprehensive study, offer valuable lessons and pave the way for global improvements in e-waste management.
The Role of Private Sector and NGOs
In addition to government efforts, the private sector and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are playing an increasingly important role in shaping the Global Landscape of E-waste Management. Through partnerships and innovative solutions, these entities contribute to the development and implementation of sustainable practices.
This expanded section provides a more thorough examination of the challenges and future prospects in the Global Landscape of E-waste Management. It aims to equip stakeholders—ranging from policymakers and industry leaders to the general public—with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate this complex landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Global Landscape of E-waste Management
What is E-waste?
E-waste, or electronic waste, refers to discarded electronic or electrical devices. This can include everything from old smartphones and laptops to household appliances like refrigerators.
Why is E-waste Management Important?
E-waste management is crucial for mitigating the environmental and health risks associated with improper disposal of electronic waste. It also offers opportunities for material recovery and recycling.
What are the Main Challenges in E-waste Management?
The main challenges include technological limitations, regulatory hurdles, and lack of public awareness. Each of these factors contributes to the complexity of effective e-waste management strategies on a global scale.
How Can I Dispose of My E-waste Responsibly?
Many cities have designated e-waste collection centers where you can drop off your old electronic devices for proper disposal or recycling. Some retailers also offer take-back programs.
What Role Do Governments Play in E-waste Management?
Governments are responsible for implementing regulations and policies that guide e-waste management. They also work on international collaborations to standardize e-waste management practices.
Are There Any Success Stories in E-waste Management?
Yes, countries like Sweden and Japan have successfully implemented e-waste management strategies. You can read more about their approaches in this comprehensive study.
This FAQ section aims to provide quick answers to common questions about the Global Landscape of E-waste Management, offering readers a convenient resource for basic information.
Conclusion: The Path Forward in the Global Landscape of E-waste Management
As we’ve explored the multifaceted aspects of the Global Landscape of E-waste Management, it’s clear that this is a pressing issue requiring immediate attention. From the challenges of technological limitations and regulatory hurdles to the promising future prospects and success stories, the landscape is complex but not insurmountable.
The key to navigating this complexity lies in a multi-stakeholder approach that involves governments, the private sector, NGOs, and the public. Through collaborative efforts, technological innovations, and public awareness campaigns, we can pave the way for more sustainable e-waste management practices on a global scale.
While challenges remain, the opportunities for creating a more sustainable and responsible approach to e-waste management are abundant. By understanding these complexities and taking proactive steps, we can contribute to a more sustainable future, both environmentally and economically.
This concludes our comprehensive guide on the Global Landscape of E-waste Management. We hope this article serves as a valuable resource for all stakeholders involved in e-waste management, equipping them with the knowledge and insights needed to make informed decisions.