The Technical Side of Laptop Recycling: What Happens Inside the Facility
The amount of electronic waste, also known as e-waste, generated worldwide has been increasing rapidly due to changes in technology, planned obsolescence, and easier accessibility to electronics. E-waste refers to electronic devices that have reached the end of their life, and it has become the fastest-growing waste stream globally. Common types of e-waste include small equipment like vacuum cleaners, microwaves, and small IT and telecommunication equipment such as cell phones and computers. Improperly managed e-waste can release toxic chemicals into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and human health.
Recycling e-waste is crucial to minimize these negative impacts and recover valuable materials. However, the challenges of recycling e-waste are complex. The process involves dismantling electronics, separating different materials, and the potential environmental and health hazards associated with informal recycling facilities. To address these challenges, specialized recycling facilities play a vital role. Let’s take a closer look at what happens inside a laptop recycling facility.
Inside a laptop recycling facility, the electronic waste goes through a systematic process to ensure proper disposal and material recovery. This process involves several stages, including collection, sorting, dismantling, and mechanical separation.
Continue reading to learn more about the laptop recycling process and the importance of responsible e-waste management.
Why is Electronic Waste Recycling Important?
Recycling electronic waste is essential for sustainable waste management and has numerous benefits. Improperly managed e-waste can release toxic chemicals into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Recycling e-waste allows for the recovery of valuable materials such as gold, copper, and plastic, reducing the need for mining new resources and minimizing the environmental impact of production.
Additionally, recycling and reuse of e-waste contribute to job creation and the overall sustainability of the electronics industry. By diverting electronic waste from landfills and incinerators, we can prevent hazardous substances from leaching into the soil and water, thereby protecting the environment and public health.
Furthermore, the recycling of electronic waste reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with the extraction and manufacturing of new electronic products. It also conserves energy and conserves resources by reusing materials that have already been extracted and processed.
Dangers of Improper E-Waste Disposal
Improper disposal of electronic waste can have significant consequences. When e-waste is incinerated or ends up in landfills, toxic substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium can contaminate the environment, leading to soil and water pollution. These hazardous materials can bioaccumulate in the food chain, posing a threat to not only wildlife but also humans who consume contaminated food and water.
Furthermore, electronic devices often contain valuable and scarce resources, such as rare earth metals, which are mined at great environmental and human cost. By recycling e-waste, we can recover these valuable materials and reduce the need for destructive mining practices.
“Recycling electronics not only benefits the environment but also fuels the circular economy, where resources are reused, reducing the demand for new resources and minimizing waste generation,” said Dr. Emma Green, a leading expert in sustainable waste management.
To address the growing e-waste problem, greater awareness is needed among individuals, businesses, and governments. Improved management systems and responsible recycling practices can ensure the safe and efficient handling of electronic waste.
The Benefits of Electronic Waste Recycling
The benefits of electronic waste recycling extend beyond environmental protection. It also contributes to job creation and economic growth. According to a report by the World Economic Forum, the global recycling sector employs an estimated 18 million individuals, offering opportunities for formal employment and income generation.
The recycling and reuse of electronic waste also support the overall sustainability of the electronics industry. By incorporating recycled materials into new products, manufacturers can reduce their reliance on virgin resources and decrease their carbon footprint.
Advantages of Electronic Waste Recycling
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Protection | Prevents toxic substances from polluting the environment and conserves resources. |
| Job Creation | Provides employment opportunities and economic benefits. |
| Reduced Carbon Footprint | Saves energy and reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with mining and production. |
| Circular Economy | Supports the reuse of materials, reducing the demand for new resources. |
By embracing electronic waste recycling, we can contribute to sustainable waste management, protect the environment, and build a greener future for generations to come.
The Challenges of Recycling Electronic Waste
Despite the importance of recycling e-waste, there are significant challenges associated with electronic waste recycling programs and increasing diversion rates. The hazardous materials present in e-waste can create difficulties in the recycling process, requiring careful disassembly. Informal recycling facilities in developing countries often lack proper environmental and occupational safety measures, leading to severe environmental impacts.
The wide variety of electronic products and the mixed materials they contain make recycling e-waste complex and costly. Municipal and private electronic waste collections may have different acceptance criteria, further complicating the recycling process. However, there are systems in place to address these challenges and improve e-waste recycling practices.
The Complexity of E-waste Recycling
E-waste recycling is a complex process due to the wide range of electronic devices and the diverse materials they contain. From smartphones and laptops to household appliances and televisions, each electronic device presents unique challenges for recycling. The mixture of plastics, metals, circuit boards, batteries, and other components requires careful separation and specialized machinery.
| Challenges | Impacts |
|---|---|
| Lack of standardized recycling processes | Increases costs and reduces efficiency |
| Hazardous materials | Pose risks to human health and the environment |
| Inadequate recycling infrastructure | Complicates the e-waste collection and recycling process |
| Limited public awareness | Results in low e-waste recycling rates |
The complexity of recycling e-waste requires the collaboration of government, industry, and consumers to establish effective electronic waste recycling programs that address these challenges.
“Proper recycling of electronic waste is crucial for sustainable waste management. By overcoming the challenges associated with e-waste recycling, we can protect the environment, conserve valuable resources, and create a greener future.”
E-waste recycling programs and initiatives focus on improving collection systems, promoting responsible disposal practices, and raising public awareness. Strong regulations and enforcement are essential to ensure the proper handling of hazardous waste and the safe operation of recycling facilities. Enhanced research and development efforts are also contributing to the development of innovative technologies for more efficient and cost-effective e-waste recycling.
By addressing the challenges of e-waste recycling and supporting electronic waste recycling programs, we can work towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
The Laptop Recycling Process Flowchart
The laptop recycling process follows a step-by-step flowchart, ensuring proper e-waste management. It involves several stages, including collection, sorting, dismantling, mechanical separation, and recovery. Let’s delve into each step in detail:
- Collection: Electronic products, including laptops, are collected through various means such as recycling bins, collection locations, take-back programs, or on-demand collection services. This ensures convenient and responsible disposal of e-waste.
- Sorting: Once collected, the e-waste is taken to specialized electronics recyclers for storage. At this stage, manual sorting is performed to separate different types of devices and components.
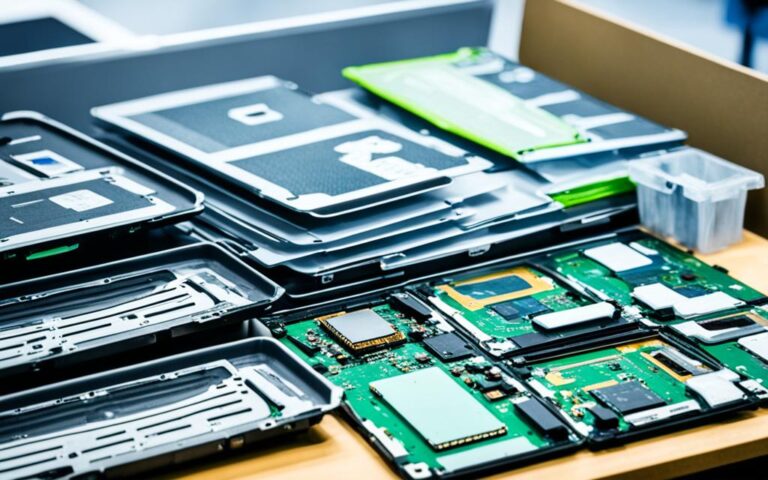
- Dismantling: In order to extract valuable materials and ensure proper disposal of hazardous components, the laptops undergo meticulous dismantling. Batteries, bulbs, and salvageable components are removed for separate treatment, reducing environmental risks.
- Shredding: The e-waste is then shredded into small pieces using specialized equipment. This process enables accurate sorting of materials in subsequent steps of the recycling process.
- Mechanical Separation: The shredded e-waste undergoes mechanical separation techniques, including magnetic and water separation. These methods help separate different materials, such as plastics, metals, and circuit boards, facilitating effective recycling.
- Recovery: Finally, the recovered materials, including precious metals like gold, copper, and valuable plastics, are prepared for sale and reuse. This contributes to the circular economy, reduces the need for raw material extraction, and minimizes the environmental impact of electronic production.
By following this laptop recycling process flowchart, we can ensure responsible e-waste management, minimize environmental harm, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
| Advantages of Laptop Recycling Process | Disadvantages of Laptop Recycling Process |
|---|---|
| 1. Reduces electronic waste buildup and associated environmental hazards | 1. Requires specialized equipment and facilities |
| 2. Enables recovery of valuable materials, reducing the need for mining | 2. Complex process requiring skilled labor and expertise |
| 3. Contributes to the circular economy and sustainability | 3. Potential challenges in handling hazardous components |
Conclusion
Laptop recycling and responsible e-waste management play a pivotal role in creating a greener future. By recycling electronic waste, we not only prevent the release of toxic chemicals into the environment but also recover valuable materials, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy. Additionally, the process of e-waste recycling creates job opportunities and strengthens the overall sustainability of the electronics industry.
However, there are challenges that need to be addressed. Hazardous materials present in e-waste require careful handling, and the complexity of recycling processes calls for improved regulations and responsible recycling practices. Efforts should be made to ensure that all e-waste recycling facilities adhere to proper environmental and occupational safety measures.
By understanding the technical side of laptop recycling and supporting responsible e-waste management, we can make a significant impact in creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly world. Together, let’s embrace the importance of recycling electronic waste and work towards a future where every laptop finds its way to a recycling facility, and e-waste is managed responsibly. Join us in building a greener future through laptop recycling.
FAQ
What is electronic waste?
Electronic waste, or e-waste, refers to electronic devices that have reached the end of their life and are no longer in use. This can include items such as laptops, cell phones, microwaves, and vacuum cleaners.
Why is recycling electronic waste important?
Recycling electronic waste is important for sustainable waste management. Improperly managed e-waste can release toxic chemicals into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Recycling allows for the recovery of valuable materials and reduces the need for mining new resources.
What are the challenges of recycling electronic waste?
The challenges of recycling electronic waste include the complex process of dismantling electronics, separating different materials, and the potential environmental and health hazards associated with informal recycling facilities.
What is the laptop recycling process?
The laptop recycling process typically follows a step-by-step flowchart. It starts with the collection of electronic products through recycling bins or collection programs. The collected e-waste is then taken to specialized recyclers for sorting and dismantling. The materials are separated using mechanical methods and prepared for sale and reuse.
How does laptop recycling contribute to a greener future?
Laptop recycling helps prevent the release of toxic chemicals into the environment and allows for the recovery of valuable materials. It also creates job opportunities and strengthens the sustainability of the electronics industry.