The Business Case for Server Recycling Programs
Welcome to the era of rapid technological advancement and digital transformation. As businesses strive to stay ahead in a competitive landscape, the use of electronics has become ubiquitous and indispensable. However, this technological boom has brought with it a grave concern – electronic waste, or e-waste.
E-waste encompasses a wide range of discarded electronic devices, such as computers, servers, monitors, tablets, printers, and cell phones. Unfortunately, the improper disposal of these devices has led to alarming environmental and health risks. Chemicals like lead, mercury, and flame retardants found in e-waste contaminate landfills, water supplies, and land, posing significant threats to ecosystems and human health.
According to the 2020 UN Global E-waste Monitor, only a mere 17.4% of e-waste is recycled, making it the largest waste stream globally. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for sustainable solutions and environmental strides. Server recycling programs play a crucial role in tackling this issue while also presenting a compelling business case for organizations.
Through responsible e-waste management practices, businesses contribute to the preservation of our planet, aligning their operations with the sustainability agenda. Moreover, by recycling servers and other electronic equipment, valuable materials can be recovered, reducing the strain on natural resources and recovering an estimated $47 billion in lost value.
These business server recycling programs not only enhance environmental sustainability but also enable companies to enhance their brand image and reputation. Clients, customers, and shareholders increasingly expect organizations to demonstrate their commitment to responsible e-waste management and overall sustainability. By embracing server recycling programs, businesses can meet these expectations, attract environmentally conscious customers, and drive positive change.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the hidden risks of e-waste, explore the approaches taken by companies to address this challenge, and examine the business risks associated with inadequate e-waste management. We will also discuss the importance of embracing responsible e-waste management and the vital role businesses play in it. Let’s navigate the world of e-waste together and uncover how sustainable practices and server recycling programs can lead to a brighter, greener future for all.
The Hidden Risks of E-waste
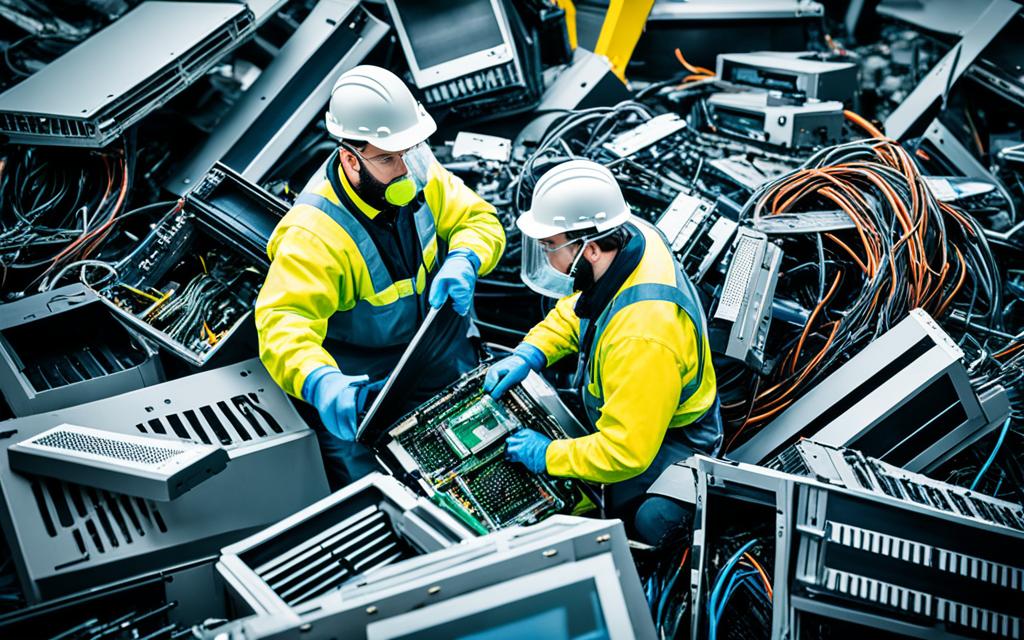
E-waste poses significant environmental impacts and health and safety risks. The improper disposal of electronic waste contaminates landfills and has adverse effects on water supplies and land. Toxic chemicals found in e-waste, such as lead, mercury, and flame retardants, can seep into the soil and water, posing long-term threats to ecosystems and human health.
“The recycling process itself exposes workers to physical injuries and airborne contaminants,” warns the 2020 UN Global E-waste Monitor. This further emphasizes the health and safety impacts associated with e-waste recycling operations. The World Health Organization has linked e-waste exposure to adverse health outcomes, including thyroid dysfunction, birth abnormalities, and decreased lung function, particularly among children.
“E-waste contains hazardous chemicals that can harm the environment and endanger human lives. Improper disposal and recycling practices pose significant risks to both ecosystems and communities,” states the 2020 UN Global E-waste Monitor.
To gain a better understanding of these risks, let’s take a closer look at the environmental and health impacts of e-waste:
Environmental Impacts of E-waste
E-waste, when improperly discarded, contributes to land pollution and water contamination. The hazardous materials present in electronic devices can seep into the soil and water, affecting the health of plants, animals, and humans.
Landfills containing e-waste release toxic substances into the environment, posing a threat to ecosystems and wildlife. The leaching of heavy metals and other hazardous chemicals can pollute groundwater, making it unsafe for consumption and endangering aquatic life.
Health and Safety Impacts of E-waste
Exposure to e-waste can have detrimental effects on human health. The release of hazardous substances from electronic devices during improper dismantling, recycling, or disposal processes can lead to severe health complications.
Workers involved in e-waste recycling are particularly vulnerable to physical injuries and exposure to airborne contaminants. The lack of proper safety measures and protective equipment puts them at risk of respiratory diseases, skin conditions, and injuries from handling sharp objects and toxic chemicals.
E-waste Impacts on Communities
Communities living near e-waste recycling facilities are at a higher risk of environmental contamination and health issues. The release of pollutants during recycling operations can contaminate the air, water, and soil, impacting the well-being of nearby residents.
Children, in particular, are susceptible to the adverse effects of e-waste exposure due to their developing immune systems. Studies have found associations between e-waste exposure and thyroid dysfunction, birth abnormalities, and decreased lung function in children.
It is crucial to address these hidden risks and implement responsible e-waste management strategies that prioritize both environmental preservation and the well-being of communities.
Approaches to the E-waste Challenge
Companies are implementing various strategies to address the e-waste challenge and mitigate associated risks. These approaches include:
- Due diligence on downstream recycling vendors: Companies are conducting thorough assessments of their recycling partners to ensure that they adhere to proper e-waste management practices. This involves evaluating their recycling capabilities, certifications, and track record in environmental compliance. By collaborating with reputable vendors, companies can ensure that their e-waste is disposed of responsibly and in compliance with regulations.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs: EPR programs place the responsibility for managing a product’s entire lifecycle, including its disposal, on the producer. This means that companies are accountable for the collection, recycling, and safe disposal of their electronic products once they reach the end of their life. Implementing EPR programs encourages manufacturers to design products with recycling in mind, as they are incentivized to minimize their environmental impact and increase the recyclability of their products.
- Setting internal corporate standards: Companies are establishing internal policies and standards to govern their e-waste management practices. These standards outline the company’s commitment to responsible disposal, recycling, and resource recovery. By setting clear guidelines, companies can ensure consistent and sustainable e-waste management across their operations.
For example, a leading wearables manufacturer engaged in strategic guidance to manage e-waste risks by partnering with ERM, a global sustainability consultancy. This collaboration helped them develop robust e-waste management practices that align with their sustainability objectives.
Another technology company improved its oversight of third-party recyclers through a global recycler verification program. This initiative involved thoroughly vetting their recycling partners to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and responsible e-waste handling.
Moreover, companies are also responding to regulatory actions and market pressures by committing to ambitious climate and zero-waste goals. These commitments drive the sustainable management of e-waste and demonstrate a company’s dedication to environmental stewardship.
The Business Risks of E-waste
Companies that fail to address e-waste risks face significant business risk. Inadequate handling of e-waste can lead to reputational damage and regulatory non-compliance, which can have severe consequences for businesses. To avoid these risks, it is crucial for companies to prioritize responsible e-waste management and implement appropriate strategies.
Regulatory actions, such as the European Union’s Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive recast, are putting pressure on companies to take responsibility for their e-waste. These regulations are pushing for product takeback and resource recovery to ensure sustainable disposal practices. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in legal consequences and penalties.
In addition to regulatory action, customer expectations and shareholder demands are driving companies to adopt climate and zero-waste goals. Customers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of the products they purchase and expect companies to demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. Shareholders, on the other hand, are advocating for responsible business practices that align with their own ethical values.
Companies that fail to meet these expectations and demands may face financial and operational challenges. Reputational damage can lead to a loss of customer trust and loyalty, impacting sales and revenue. Failure to embrace sustainable practices can also hinder business growth and diminish shareholder confidence, affecting the overall value of the company.
The risks associated with e-waste extend beyond the immediate business impact. The management of e-waste is crucial for achieving broader business objectives and long-term sustainability. By actively participating in sustainable solutions and taking proactive measures to address e-waste risks, companies can ensure their continued success in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
“The e-waste challenge poses risks to broader business objectives and requires proactive management and participation in sustainable solutions.”
| Risks | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reputational damage | Loss of customer trust and loyalty, negative brand image |
| Regulatory non-compliance | Legal consequences, fines, penalties |
| Financial challenges | Decreased sales, increased operational costs |
| Operational challenges | Disruption to supply chain, inefficient waste management processes |
| Shareholder dissatisfaction | Diminished confidence, decreased company value |
Embracing Responsible E-waste Management
To effectively manage the e-waste stream, companies must take a proactive approach towards handling and processing electronic waste. By understanding the costs associated with e-waste and quantifying its impact on the business, companies can identify opportunities for improvement and make informed decisions.
“Quantifying the e-waste stream and costs helps companies understand the impact on their business and identify improvement opportunities.”
Transparency in e-waste handling and processing is essential for responsible disposal and reducing additional risks. This includes implementing proper protocols and collaborating with certified recyclers to ensure that e-waste is managed in an environmentally-friendly manner.
“Transparency in e-waste handling and processing ensures responsible disposal and reduces additional risks.”
Companies can also explore the concept of circularity, which involves redesigning products to facilitate the recovery of valuable components. By embracing circularity, businesses contribute to sustainability goals and minimize the environmental impact of e-waste.
“Exploring circularity involves redesigning products for easier recovery of valuable components, which contributes to sustainability goals.”
Embracing responsible e-waste management is not only aligned with a company’s sustainability objectives but also creates a strategic business advantage. By demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship, companies can attract environmentally-conscious customers, enhance their brand image, and meet sustainability expectations.
“Embracing responsible e-waste management aligns with a company’s sustainability objectives and creates a strategic business advantage.”
Benefits of Embracing Responsible E-waste Management
- Minimizes environmental impact
- Reduces costs associated with e-waste management
- Enhances brand image and reputation
- Attracts environmentally-conscious customers
- Meets sustainability expectations
Comparison of Different E-waste Management Approaches
| Approach | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Quantifying e-waste stream and costs | Understanding the impact on the business and identifying improvement opportunities | – Minimizes financial losses – Identifies areas for optimization |
| Transparency in handling and processing | Implementing responsible disposal protocols and collaborating with certified recyclers | – Reduces environmental risks – Ensures compliance with regulations |
| Exploring circularity | Redesigning products for easier recovery of valuable components | – Contributes to sustainability goals – Maximizes resource efficiency |
By embracing responsible e-waste management, companies can take significant strides towards achieving their sustainability goals while contributing to a more sustainable future.
The Role of Businesses in E-waste Generation
Businesses play a significant role in e-waste generation, particularly due to the increasing reliance on technology. However, many companies are unaware of where their e-waste ends up, leading to irresponsible disposal methods. It is crucial for businesses to prioritize responsible e-waste management strategies to address this pressing issue.
One of the key steps businesses can take is to educate their employees about proper e-waste disposal methods. By creating awareness and providing guidance, companies can ensure that their workforce understands the importance of responsible e-waste management and takes necessary actions.
“Our employees are our greatest asset, and it is our responsibility to equip them with the knowledge and tools to contribute to a sustainable future. That includes educating them on the proper disposal of electronic waste.”
In addition to education, implementing tracking systems for IT devices can help businesses keep a record of their electronic equipment throughout its lifecycle. This enables better tracking of e-waste and ensures that it is disposed of responsibly or recycled through certified channels.
Furthermore, businesses can explore partnerships with certified e-waste recyclers. By collaborating with reputable organizations, companies can ensure that their e-waste is managed responsibly, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource recovery.
Responsible e-waste management not only helps reduce the environmental consequences of irresponsible e-waste disposal but also has several other benefits for businesses. It enhances brand image by showcasing a commitment to sustainability, which can attract environmentally conscious customers. It also aligns with sustainability expectations set by various stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulators.
| Benefits of Responsible E-waste Management for Businesses | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Enhanced brand image | Attracts environmentally conscious customers |
| Compliance with sustainability expectations | Meets stakeholder demands (customers, investors, regulators) |
| Reduced environmental impact | Addresses the consequences of irresponsible e-waste disposal |
Conclusion
The growing problem of e-waste calls for sustainable solutions. By embracing responsible e-waste management, businesses can minimize their environmental impact, reduce costs, and improve performance. Electronic waste recycling and the implementation of e-waste legislation are crucial components of effective e-waste management.
To strike a balance between sustainability and technological advancement, businesses must meet the demands of customers, investors, and regulatory requirements. Prioritizing sustainable practices gives companies a competitive edge in the market, attracts top talent, and contributes to building a more sustainable future.
It is imperative for businesses to recognize their role in addressing e-waste challenges. Through education of employees about proper disposal methods, the implementation of tracking systems for IT devices, and partnerships with certified e-waste recyclers, companies can ensure responsible e-waste management. This not only reduces environmental impact but also enhances brand image and meets sustainability expectations.
In summary, sustainable solutions, such as electronic waste recycling and compliance with e-waste legislation, are vital for addressing the growing e-waste problem. By prioritizing responsible e-waste management, businesses can make a positive impact on the environment, reduce costs, and thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
FAQ
What is the business case for server recycling programs?
Server recycling programs are essential for businesses to make sustainability and environmental strides. By recycling servers, companies can minimize electronic waste (e-waste) and reduce their environmental impact. Additionally, server recycling programs offer opportunities for cost savings and improved performance.
What are the hidden risks of e-waste?
E-waste poses significant environmental impacts, as well as health and safety risks. Improper disposal of e-waste can contaminate landfills, impact water supplies, and contribute to land pollution. It also exposes workers to physical injuries and airborne contaminants. Furthermore, the presence of hazardous chemicals in e-waste, such as lead, mercury, and flame retardants, can lead to adverse health outcomes, including thyroid dysfunction and birth abnormalities.
What approaches can companies take to address the e-waste challenge?
Companies can adopt various approaches to mitigate e-waste risks. These include conducting due diligence on downstream recycling vendors, implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, and setting internal corporate standards. Companies can also engage in strategic guidance, improve oversight of their third-party recycler network, and commit to climate and zero-waste goals.
What are the business risks of e-waste?
Companies that fail to address e-waste risks face potential business risks, including reputational damage and regulatory non-compliance. Regulatory actions, such as the European Union’s Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive recast, are pushing for product takeback and resource recovery. Customers and shareholders are also pressuring companies to adopt climate and zero-waste goals. Failure to meet these expectations can result in financial and operational challenges.
How can businesses embrace responsible e-waste management?
To embrace responsible e-waste management, businesses need to quantify their e-waste stream and associated costs, understand how e-waste is handled and processed, and assess options for circularity. This includes redesigning products for easier recovery of valuable components. By aligning with their sustainability goals, companies gain a strategic business advantage while reducing their environmental impact.
What is the role of businesses in e-waste generation?
Businesses play a significant role in e-waste generation, especially with the increasing reliance on technology. However, many companies are unaware of where their e-waste ends up, leading to improper disposal methods. It is crucial for businesses to prioritize responsible e-waste management by educating employees about proper disposal methods, implementing tracking systems for IT devices, and exploring partnerships with certified e-waste recyclers.
What are the sustainable solutions for e-waste management?
Embracing responsible e-waste management involves electronic waste recycling and implementing e-waste legislation. These are crucial components of effective e-waste management. By balancing sustainability with technological advancement and meeting the demands of customers, investors, and regulatory requirements, businesses can minimize their environmental impact, reduce costs, and improve performance.