Recycling Phones and Tablets: A Step Towards Zero Waste
Cell phones, tablets, and laptops have become vital aspects of our daily lives, but when they reach the end of their usefulness, it is essential to consider their environmental impact. Recycling these devices is not only responsible but also a crucial step in reducing electronic waste.
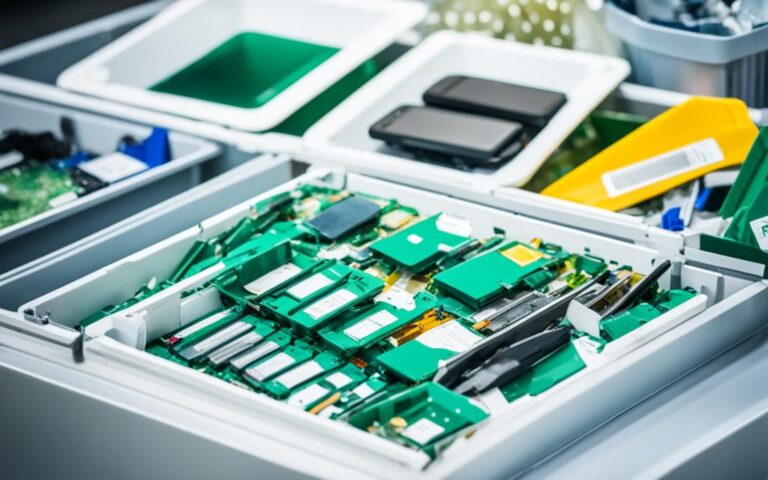
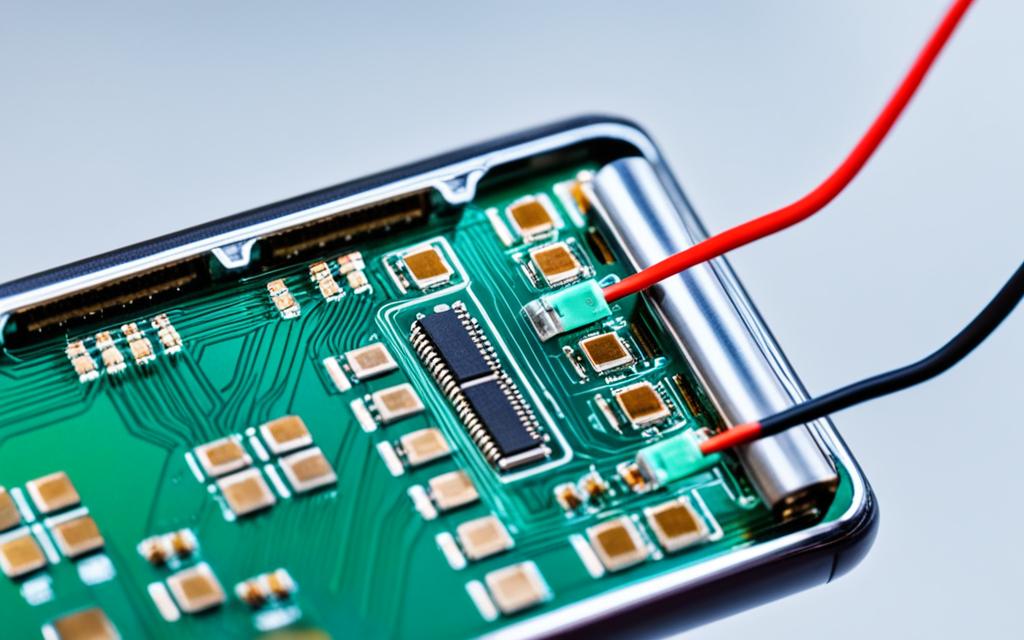
Understanding the components of these gadgets, such as batteries, screens, circuit boards, plastics, and rare earth metals, is the first step towards sustainable recycling.
The Anatomy of Electronic Devices
Electronic devices like cell phones, tablets, and laptops are made up of various components. Understanding the different parts that make up these devices is crucial for effective recycling and resource recovery.
Cell Phone Components
Cell phones consist of several key components:
- Batteries: The heart of cell phones, batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries, contain valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
- Screens: Made of glass and other recyclable materials, screens can be replaced or reused, reducing the need for new manufacturing.
- Circuit Boards: These boards contain valuable metals like copper, gold, silver, steel, and aluminum, which can be extracted and recycled.
- Plastic: Used for the outer casing of many devices, plastic can be recycled and repurposed for various applications.
- Rare Earth Metals: Though present in small quantities, rare earth metals are used in various components and can be recovered for future use.
Tablet Components
Tablets also have similar components, including:
- Batteries: Like cell phones, tablets use lithium-ion batteries containing valuable materials.
- Screens: Tablets utilize screens, typically made of glass, that can be reused or recycled.
- Circuit Boards: Circuit boards found in tablets contain metals that can be extracted for recycling.
- Plastic: Plastic is used for the casing of tablets, which can be recycled and repurposed.
- Rare Earth Metals: Tablets may also contain small amounts of rare earth metals for various functionalities.
Laptop Components
Laptops are complex devices with components such as:
- Batteries: Laptop batteries, often lithium-ion, store and provide power to the device.
- Screens: Laptops feature screens made of recyclable materials, such as glass and metals.
- Circuit Boards: Circuit boards found within laptops contain valuable metals for recycling and material recovery.
- Plastic: Plastic is used for the housing and structural components of laptops.
- Rare Earth Metals: Some laptops may contain rare earth metals in specific parts for enhanced performance.
Understanding the anatomy of electronic devices is essential for responsible disposal, recycling, and resource recovery. By recovering valuable materials from these devices, we can reduce the dependence on raw materials, minimize environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Recycling Process for Electronic Devices
Recycling electronic devices involves a multi-step process. Electronic devices, including cell phones, tablets, and laptops, are collected from various sources, such as consumers, businesses, and manufacturers. These devices are then taken to recycling facilities where they undergo dismantling and component sorting based on material type.
The components of electronic devices, such as batteries, screens, circuit boards, and plastics, are methodically sorted to ensure efficient recycling. Some devices may require a shredding process to break them down into smaller pieces for easier handling and processing.
Techniques like material recovery are employed to extract valuable materials like metals, glass, and plastics for reuse. These materials can be transformed into new electronic components, reducing the need for virgin resources and minimizing waste. Components that cannot be recycled are disposed of safely to prevent any negative environmental impact.
Here is a breakdown of the recycling process for electronic devices:
- Collection from consumers, businesses, and manufacturers
- Dismantling of devices
- Sorting components based on material type
- Shredding to break devices into smaller pieces
- Material recovery to extract valuable materials
- Disposal of non-recyclable components
It is important to note that each step of the recycling process is conducted with utmost care and adherence to environmental regulations. Recycling electronic devices not only helps conserve valuable resources but also reduces the environmental impact of electronic waste.
By recycling electronic devices, we can create a sustainable electronic ecosystem that promotes responsible e-waste management. The recovery and reuse of valuable materials contribute to a circular economy where resources are conserved and waste is minimized.
How Recycling Repurposes—and Preserves—Our Resources
Recycling electronic devices allows for the repurposing and preservation of valuable resources. When old gadgets are recycled, precious metals like gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements are recovered and reused in the manufacturing of new electronic components. This not only reduces the need for extracting and processing raw materials but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with their extraction.
One of the significant benefits of recycling electronics is the reduction in the demand for new plastic. By recycling and reusing plastic from old devices, the production of new casings and components can be achieved without relying heavily on virgin plastic materials. This helps to mitigate the negative environmental consequences of plastic production and disposal.
Glass from old screens is another recyclable component in electronic devices. Instead of ending up in landfills, this glass can be melted down and efficiently used to produce new screens or other glass components. By incorporating recycled glass, the industry can reduce energy consumption associated with glass production and decrease the greenhouse gas emissions produced during the manufacturing process.
Additionally, lithium-ion batteries found in many electronic devices have the potential to be reconditioned and reused in less demanding applications. This extends the life of the batteries and reduces the need for the extraction and production of new lithium-ion batteries. By promoting battery reuse, recycling contributes to a more sustainable and circular approach to managing electronic waste.
The recovery of rare earth elements is another crucial aspect of recycling electronic devices. These elements are vital components in various high-tech applications, including renewable energy technologies, electric vehicles, and electronics. By recycling electronic devices, the supply of rare earth elements can be maintained and conserved, reducing the need for environmentally destructive mining practices.
Lastly, recovered circuit boards can be refurbished or have valuable metals extracted for recycling. These metals, such as copper, gold, silver, steel, and aluminum, can be reused in the production of new electronic components. Recycling circuit boards not only conserves these precious metals but also reduces the need for extracting new resources, leading to a more sustainable electronic industry.
The Benefits of Recycling Electronics:
- Repurposing valuable metals like gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements
- Reducing the demand for new plastic through recycling and reuse
- Melting down glass from old screens for manufacturing new screens or glass components
- Reconditioning and reusing lithium-ion batteries in less demanding applications
- Conserving and recovering rare earth elements crucial for high-tech applications
- Refurbishing circuit boards and extracting valuable metals for recycling
Comparison of Recycling Benefits
- Repurposing valuable metals like gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements
- Reducing the demand for new plastic through recycling and reuse
- Melting down glass from old screens for manufacturing new screens or glass components
- Reconditioning and reusing lithium-ion batteries in less demanding applications
- Conserving and recovering rare earth elements crucial for high-tech applications
- Refurbishing circuit boards and extracting valuable metals for recycling
Comparison of Recycling Benefits
| Benefits | Recycling Electronic Devices | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Repurposing Valuable Metals | Conserves precious metals and reduces the need for new resource extraction | Reduces carbon emissions and ecosystem disruption from mining |
| Reducing Plastic Demand | Recycles plastic for new casings and components, reducing plastic production | Decreases plastic pollution and fossil fuel consumption in plastic production |
| Glass Recycling | Melts down glass for new screens or glass components, reducing energy consumption | Minimizes greenhouse gas emissions from glass production |
| Battery Reuse | Reconditions and reuses lithium-ion batteries, extending their lifespan | Reduces the need for new battery production and disposal |
| Rare Earth Element Recovery | Recovers and conserves rare earth elements for high-tech applications | Decreases reliance on destructive mining practices |
| Circuit Board Recycling | Refurbishes circuit boards and extracts valuable metals for recycling | Reduces the need for new resource extraction and associated environmental harm |
The Global Impact of Electronics Recycling
Electronic waste (e-waste) is a growing concern worldwide due to its hazardous nature and potential harm to both human health and the environment. The global significance of electronics recycling cannot be underestimated, as it plays a vital role in mitigating the environmental impact of e-waste.
When electronic devices are recycled, the demand for raw materials is reduced, leading to fewer resources extracted from the earth. This has significant implications for preserving natural habitats, reducing deforestation, and protecting biodiversity. Additionally, the recycling of electronic devices helps to mitigate the carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing of new devices. By repurposing existing materials, energy-intensive processes involved in the extraction and production of raw materials can be minimized, leading to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach.
Furthermore, electronics recycling contributes to the establishment of a circular economy. It promotes the reuse and recovery of valuable components in electronic devices, preventing them from becoming waste. As a result, the lifespan of these components is extended, reducing the need for new production. This closed-loop system not only conserves resources but also reduces the generation of e-waste, ensuring a more sustainable future for our planet.
By responsibly disposing of and recycling electronic devices, we can make a positive impact on the environment and contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to e-waste management.
The table below provides a summary of the global significance of electronics recycling and its environmental impact:
| Benefits of Electronics Recycling | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduces demand for raw materials | Preserves natural habitats and reduces deforestation |
| Lowers carbon footprint | Minimizes energy-intensive processes for raw material extraction |
| Contributes to a circular economy | Promotes reuse and recovery of valuable components |
| Extends lifespan of components | Reduces generation of e-waste |
By recognizing the global significance of electronics recycling and the environmental impact of e-waste, individuals, businesses, and governments can take proactive steps towards responsible e-waste management. Together, we can create a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future for generations to come.
The Role of Consumers
Consumers hold significant responsibility in the electronics recycling process. It is crucial for individuals to adopt a proactive approach towards responsible disposal to minimize the environmental impact of electronic waste. Simply discarding devices in the trash is not a sustainable solution. Instead, consumers should actively seek out certified electronics recycling centers or drop-off locations in their communities.
When recycling electronic devices, it is also important to take measures to protect personal data. Erasing all personal information before recycling a device ensures data security and mitigates the risk of identity theft. Whether it’s through factory resets, data wiping tools, or contacting the device manufacturer for assistance, consumers must take the necessary steps to safeguard their privacy.
As a society, we can encourage the ethos of reuse and repurposing by finding creative ways to breathe new life into old devices. Upcycling electronic devices not only reduces waste but also extends their useful lifespan. There are numerous online resources and communities that provide ideas and inspiration for repurposing old electronics, giving them a new purpose and reducing the need for new devices.
Furthermore, making informed purchasing decisions can contribute to a more sustainable electronic ecosystem. Supporting eco-friendly manufacturers who prioritize environmental stewardship and have robust recycling programs in place can have a positive impact. By choosing products from companies that follow sustainable practices, consumers can play a role in driving the industry towards a greener future.
Tips for Responsible Disposal of Devices:
- Research certified electronics recycling centers or drop-off locations in your area.
- Ensure personal data is thoroughly erased from the device before recycling.
- Explore creative ways to upcycle and repurpose old devices.
- Support eco-friendly manufacturers with strong recycling initiatives.
By embracing consumer responsibility in electronics recycling, we can all contribute to a more sustainable future and protect our planet from the harmful effects of electronic waste.
Finding Responsible E-Cyclers
When it comes to recycling your electronic devices, it is crucial to find responsible e-cyclers who prioritize proper handling and disposal. By choosing certified e-cycling programs and recycling centers that adhere to recognized standards, you can ensure that your e-waste is managed responsibly, minimizing environmental impact and preventing it from being exported to low-income countries.
Look for recycling centers or programs that display certification from reputable organizations such as R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards. These certifications guarantee that the e-cycler follows best practices and complies with strict guidelines for responsible electronics recycling.
Many stores and manufacturers also offer convenient options for recycling electronics, including drop-off locations, mail-in programs, or even pickup services. This makes it easier than ever for consumers to responsibly dispose of their devices without hassle.
The Importance of Certified E-cycling Programs
By choosing e-cyclers with certifications, you can have peace of mind knowing that your old devices are being handled in an environmentally responsible manner. Certified e-cycling programs ensure that:
- E-waste is properly and safely dismantled.
- Hazardous materials are handled and disposed of according to regulations.
- Recoverable materials are recycled and repurposed.
- E-waste is not exported to developing countries with inadequate recycling facilities.
Choosing certified e-cyclers is not only beneficial to the environment but also contributes to a more sustainable electronic ecosystem. Responsible electronics recycling helps conserve resources, reduces the demand for raw materials, and lowers the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing new devices.
Responsible electronics recycling is a collective effort that requires collaboration between consumers, manufacturers, and recycling facilities. By choosing certified e-cycling programs, you can make a positive impact and contribute to a greener future.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gWN9sUaDHHU
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| R2 (Responsible Recycling) | A certification program that promotes responsible recycling practices, ensuring that e-waste is managed safely and responsibly. |
| e-Stewards | A certification program that guarantees the responsible handling of e-waste, preventing its export to developing countries with inadequate recycling facilities. |
Conclusion
Recycling phones and tablets is a significant step towards achieving zero waste and creating a sustainable electronic ecosystem. By understanding the components of electronic devices and the recycling process, consumers can make informed decisions and contribute to responsible e-waste management. Recycling not only conserves valuable resources but also reduces the environmental impact of electronic waste. Through proper recycling and repurposing, the materials from old devices can be used to manufacture new ones, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible electronics industry.
By embracing zero waste phone and tablet recycling practices, we can minimize the negative ecological and social consequences of electronic waste. As consumers, it is our responsibility to ensure that our old devices don’t end up in landfills, but rather in certified electronics recycling centers or drop-off locations. Together, we can create a circular economy for electronic devices, where materials are reused and repurposed, reducing the need for excessive resource extraction and minimizing environmental degradation.
The sustainable electronic ecosystem that we envision is one where every consumer takes an active role in responsible disposal and recycling of electronic devices. Furthermore, supporting eco-friendly manufacturers and making informed purchasing decisions contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of the electronics industry. Let’s strive for a future where zero waste phone and tablet recycling is the norm, where our actions today shape a healthier and greener world for future generations.
FAQ
Why is it important to recycle phones and tablets?
Recycling phones and tablets is important because it helps reduce electronic waste and its harmful environmental impact. By recycling these devices, valuable resources can be repurposed and preserved, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible electronic ecosystem.
What are the components of electronic devices?
Electronic devices like phones and tablets are made up of various components. These include batteries (such as lithium-ion batteries), screens (made of glass and other recyclable materials), circuit boards (containing metals like copper, gold, silver, steel, and aluminum), plastic (used for the outer casing), and rare earth metals (present in small quantities and used in various components).
What is the process of recycling electronic devices?
The process of recycling electronic devices involves several steps. The devices are first collected from various sources, sorted based on material type, and then dismantled. Components like batteries, screens, circuit boards, and plastics are sorted, while some devices may go through a shredding process. Valuable materials like metals, glass, and plastics are recovered through techniques like material recovery and prepared for reuse, while non-recyclable components are disposed of safely.
How does recycling repurpose and preserve our resources?
Recycling repurposes and preserves valuable resources by recovering materials like gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements from old devices. These recovered materials can be used in manufacturing new electronic components. Additionally, recycled plastic can be used to produce new casings and components, reducing the demand for new plastic. Glass from old screens can be melted down and used for new screens or glass components. Lithium-ion batteries can be reconditioned and reused in less demanding applications, and circuit boards can be refurbished or have metals extracted for recycling.
What is the global impact of electronics recycling?
Electronics recycling has a significant global impact due to the growing concern over electronic waste (e-waste). By recycling electronic devices, the demand for raw materials is reduced, leading to a lower carbon footprint associated with manufacturing new devices. Additionally, responsible disposal and recycling of electronic devices contribute to a circular economy and help prevent the release of hazardous materials that can harm human health and the environment.
What is the role of consumers in electronics recycling?
Consumers play a crucial role in the electronics recycling process. It is important for consumers to responsibly dispose of their devices by finding certified electronics recycling centers or drop-off locations. Personal data should be erased before recycling a device, and upcycling or repurposing old devices is encouraged. Supporting eco-friendly manufacturers and making informed purchasing decisions also contribute to a more sustainable electronic ecosystem.
How can I find responsible e-cyclers for electronics recycling?
To find responsible e-cyclers for electronics recycling, look for e-waste recycling centers or programs that display certification from organizations such as R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards. These certifications ensure that e-waste is handled correctly and prevent its export to low-income countries. Various stores and manufacturers offer drop-off, mail-in, or pickup options for recycling electronics, making it convenient for consumers to responsibly dispose of their devices.
What is the conclusion about phone and tablet recycling?
Recycling phones and tablets is a significant step towards achieving zero waste and creating a sustainable electronic ecosystem. By understanding the components of electronic devices and the recycling process, consumers can make informed decisions and contribute to responsible e-waste management. Recycling not only conserves valuable resources but also reduces the environmental impact of electronic waste. Through proper recycling and repurposing, the materials from old devices can be used to manufacture new ones, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible electronics industry.