Spotlight on Server Recycling Techniques
As the world becomes more conscious of environmental sustainability, the need for efficient server recycling techniques is paramount. Proper server disposal methods and environmentally friendly server recycling practices are essential for minimizing e-waste and reducing the impact on our planet. In this article, we will explore the importance of server recycling, the responsible disposal of electronic waste, sustainable server recycling techniques, the future of server recycling, and key takeaways for optimizing e-waste management.
Key Takeaways
- Recycling and reusing servers is crucial for sustainable e-waste management.
- Proper disposal of electronic waste is essential for minimizing environmental harm.
- Sustainable server recycling techniques focus on maximizing resource recovery and minimizing environmental impact.
- The future of server recycling lies in technological advancements and innovation.
- By partnering with certified recyclers and investing in sustainable server recycling technologies, companies can optimize e-waste management.
Responsible Electronic Waste Disposal
Proper disposal of electronic waste is crucial for minimizing environmental harm and promoting sustainable IT waste management practices. Ethical server decommissioning ensures secure data destruction and responsible equipment disposal. To achieve this, companies should partner with certified recyclers who can handle their e-waste in compliance with regulations.
Recycling practices for e-waste involve dismantling, sorting, and processing materials for recycling or reusing. This helps recover valuable materials like precious metals and reduces the need for resource-intensive mining. It is important to use secure data destruction methods to protect sensitive information and prevent data breaches during server disposal.
“The circular economy approach promotes the reuse and recycling of electronic waste, minimizing resource extraction and environmental impact.”
The circular economy approach promotes the reuse and recycling of electronic waste, minimizing resource extraction and environmental impact. By adopting this approach, companies can contribute to a closed-loop system where materials from old servers are used to produce new electronic devices or other industries. Recycling electronics not only conserves resources but also helps address the growing problem of electronic waste.
| Benefits of Responsible E-Waste Recycling | Challenges of IT Waste Management |
|---|---|
|
|
Responsible electronic waste disposal is a crucial aspect of sustainable IT practices. By following ethical server decommissioning procedures, companies can ensure secure data destruction and responsible equipment disposal. Recycling e-waste not only helps recover valuable materials but also minimizes environmental impact and promotes a circular economy.
Sustainable Server Recycling Techniques
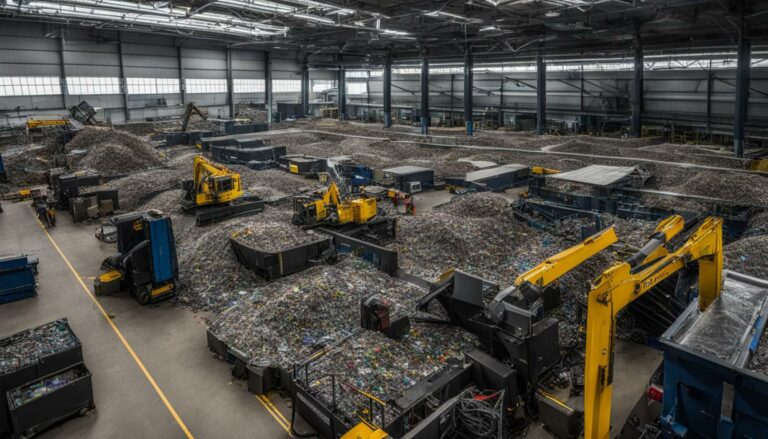
Sustainable server recycling techniques are crucial in minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource recovery. These techniques focus on efficient separation and recovery of valuable materials from decommissioned servers, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy. Advanced recycling technologies enable the proper handling and treatment of server equipment, ensuring that it does not end up as electronic waste in landfills.
One of the key techniques used in sustainable server recycling is mechanical shredding. This process involves breaking down the servers into small pieces, facilitating the separation of various materials such as plastics, metals, and circuit boards. The shredded materials can then be further sorted and processed for recycling or reusing. Magnetic separation is another commonly employed technique, where magnets are used to separate ferrous metals from non-ferrous ones, allowing for more efficient recovery of valuable metals like copper and aluminum.
Hydrometallurgical processes also play a role in sustainable server recycling. These processes involve the use of chemicals and solvents to dissolve metals from the electronic waste, allowing for their extraction and recovery. This method is particularly effective for recovering precious metals like gold and silver. Through these advanced recycling techniques, valuable materials from servers can be recycled and used in the production of new electronic devices or other industries, reducing the need for resource extraction and promoting a more sustainable approach to server recycling.
To ensure the proper handling and recycling of servers, reverse logistics and take-back programs are vital. These programs facilitate the collection and return of decommissioned servers to certified recyclers, preventing them from being improperly disposed of or ending up in the hands of unauthorized individuals. By partnering with certified recyclers and implementing efficient server equipment recycling methods, companies can contribute to a more sustainable and responsible approach to server disposal.
<!–
–>
Table: Comparison of Sustainable Server Recycling Techniques
| Recycling Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Shredding | Breaking down servers into small pieces to facilitate material separation. |
| Magnetic Separation | Using magnets to separate ferrous and non-ferrous metals for efficient recovery. |
| Hydrometallurgical Processes | Using chemicals and solvents to dissolve metals for extraction and recovery. |
By adopting sustainable server recycling techniques, companies can contribute to a more environmentally friendly approach to e-waste management. These techniques not only minimize the impact on the environment but also promote resource conservation and the development of a circular economy. As technology continues to advance, it is important to stay up-to-date with the latest innovations in server recycling to further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of the process.
The Future of Server Recycling
As technology continues to advance, so does the need for innovative server recycling techniques. Researchers and industry experts are at the forefront of developing cutting-edge recycling technologies that aim to maximize resource recovery while minimizing environmental impact. These innovations are crucial in addressing the growing concern of electronic waste and ensuring a sustainable approach to server disposal.
One promising area of development is the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) in the recycling process. LIBS enables rapid and accurate identification of different materials within servers, allowing for more efficient sorting and separation. This technology not only streamlines the recycling process but also enhances the recovery of valuable components for reuse in new electronic devices.
“Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy is revolutionizing the server recycling industry. Its ability to quickly analyze materials and determine their composition is a game-changer,” says Dr. Emily Anderson, a leading expert in sustainable electronics recycling.
Another exciting innovation is robotic dismantling. Robots equipped with advanced sensors and artificial intelligence can disassemble servers with precision, efficiently extracting valuable components for recycling. This automated approach reduces manual labor and minimizes the risk of human error, resulting in higher recycling efficiency.
Advantages of Cutting-Edge Recycling Technologies:
- Enhanced sorting and separation of materials
- Increased recovery of valuable components
- Reduced manual labor and human error
- Improved recycling efficiency
The integration of circular economy principles into server recycling practices is also shaping the future of sustainable e-waste management. By promoting a closed-loop system, where materials are recycled and reused, the circular economy approach minimizes resource extraction and reduces environmental impact.
| Recycling Technology | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) | Rapid and accurate material identification, improved sorting efficiency |
| Robotic Dismantling | Precision dismantling, reduced manual labor |

In conclusion, the future of server recycling is driven by constant innovation and technological advancements. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and robotic dismantling are revolutionizing the industry, improving efficiency, and increasing the recovery of valuable materials. By embracing cutting-edge recycling technologies and adopting circular economy principles, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to server recycling.
Conclusion
Server recycling is crucial for optimizing e-waste management and achieving sustainable practices. By partnering with certified recyclers, companies can ensure responsible disposal and contribute to resource conservation and environmental protection. Implementing secure data destruction methods is essential to safeguard sensitive information throughout the recycling process.
Looking to the aviation industry’s aircraft recycling practices, we find a model for responsible server recycling. By decommissioning and recycling planes, specialized companies ensure proper disposal and maximize resource recovery. This approach can inspire efficient and eco-friendly server recycling techniques.
The future of server recycling holds great promise, with cutting-edge technologies and innovative approaches driving the industry forward. As researchers and experts explore new methods for recovering valuable materials and enhancing recycling processes, we can expect to see further improvements in efficiency and sustainability. Collaboration between industry stakeholders, policymakers, and recycling companies will play a vital role in developing and implementing these advancements.
Optimizing e-waste management
To optimize e-waste management, companies should prioritize the selection of certified recyclers, secure data destruction, and investment in sustainable server recycling technologies. By adhering to circular economy principles, we can create a closed-loop system that minimizes resource extraction and reduces environmental impact. Through these efforts, we can pave the way towards a more sustainable future.
FAQ
What are some sustainable server recycling techniques?
Sustainable server recycling techniques include dismantling components, sorting them for recycling or refurbishment, and utilizing advanced recycling technologies such as mechanical shredding, magnetic separation, and hydrometallurgical processes.
How can companies ensure responsible electronic waste disposal?
Companies can ensure responsible electronic waste disposal by partnering with certified recyclers, implementing secure data destruction methods, and investing in sustainable server recycling technologies.
What is the future of server recycling?
The future of server recycling holds promising innovations, such as laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and robotic dismantling, that will further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of the process.
Why is server recycling important for e-waste management?
Server recycling is important for e-waste management as it contributes to resource conservation, environmental protection, and the reduction of electronic waste in landfills.
How does server recycling benefit the environment?
Server recycling benefits the environment by recovering valuable materials like precious metals, reducing the need for resource extraction through mining, and promoting a closed-loop system in the circular economy.













I have been browsing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before.