The Evolving Landscape of IT Recycling Technologies
The world of IT recycling is constantly evolving, with new technologies and strategies being implemented to manage electronic waste. This article explores the advancements in IT recycling technologies and the impact they have on sustainable technology disposal. It highlights the importance of eco-friendly IT recycling and how it contributes to electronic waste management.
Key Takeaways
- IT recycling technologies are constantly changing and improving.
- Eco-friendly IT recycling is essential for sustainable technology disposal.
- Proper electronic waste management is crucial for environmental preservation.
- New technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain are transforming IT recycling processes.
- Consumer behavior and awareness play a significant role in shaping the future of IT recycling.
The Role of Emerging Technologies in IT Recycling
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain are revolutionizing the IT recycling industry. These advancements are creating new opportunities for sustainable technology disposal and eco-friendly IT recycling.
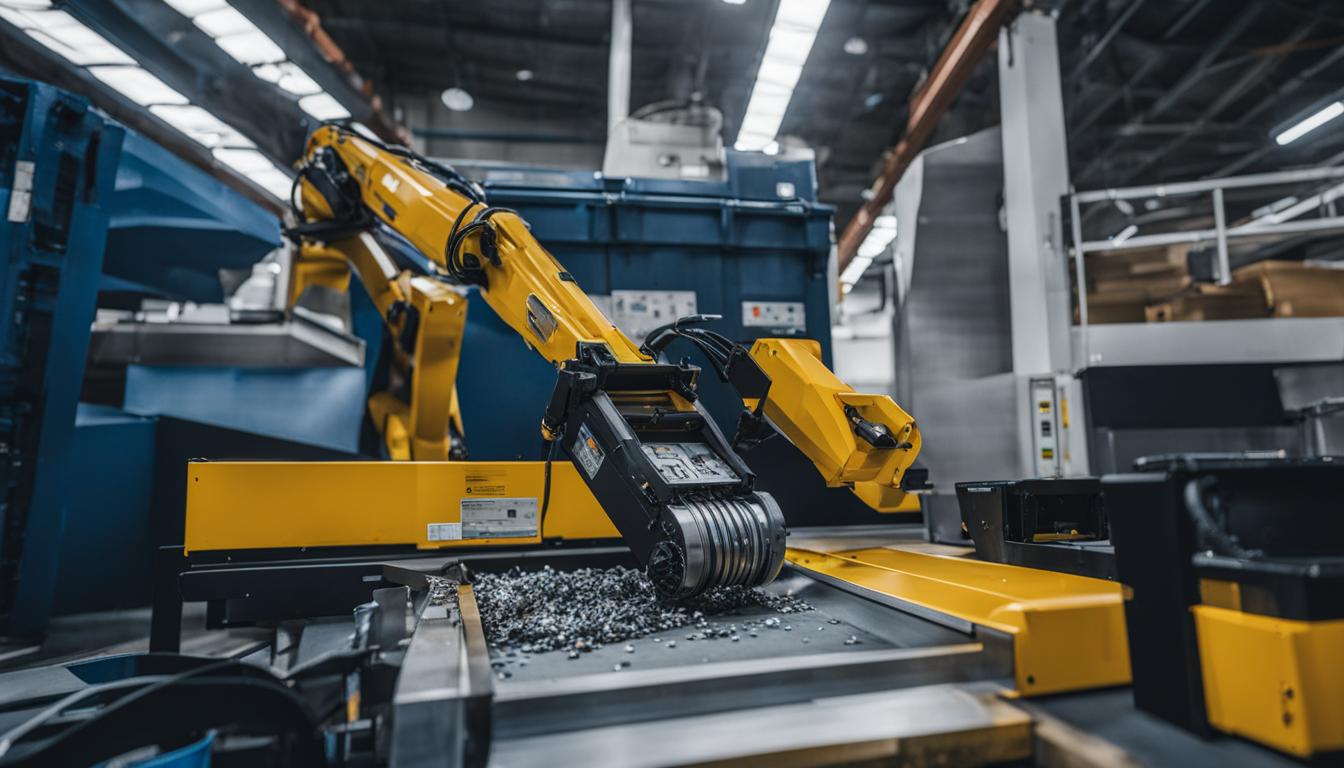
The integration of AI in IT recycling processes has brought significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy. AI-powered robotic systems can now automate the sorting and categorization of electronic waste, making the process faster and more precise. This not only enhances the recycling process but also reduces the reliance on manual labor, making it a cost-effective solution. With AI, IT recycling centers can handle larger volumes of e-waste, contributing to a more sustainable future.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another emerging technology that plays a crucial role in IT recycling. IoT devices and sensors can be embedded in electronic devices to monitor their condition in real-time. This allows IT recyclers to assess the viability of refurbishing or recycling a device based on its performance and remaining lifespan. By leveraging IoT technology, IT recycling centers can make more informed decisions, reducing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
Blockchain technology, known for its secure and transparent nature, offers immense potential for IT recycling. It can be utilized to track the entire lifecycle of electronic components, ensuring transparency in the recycling process. With blockchain, each step of IT recycling can be recorded in an immutable and tamper-proof ledger, providing stakeholders with confidence in the authenticity of the recycled products. This technology also enables traceability of the materials used in the manufacturing of electronic devices, promoting the responsible sourcing of raw materials and reducing the environmental impact.
Table: Benefits of Emerging Technologies in IT Recycling
| Emerging Technologies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Automation of sorting processes, increased efficiency, reduced reliance on manual labor |
| Internet of Things | Real-time device monitoring, informed decision-making, reduced waste |
| Blockchain | Traceability and transparency, responsible sourcing of materials, enhanced product authenticity |
As IT recycling technologies continue to evolve, the integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain offers tremendous opportunities for sustainable and eco-friendly practices. These emerging technologies are reshaping the IT recycling landscape, making it more efficient, transparent, and environmentally responsible.
The Role of Consumer Behavior in IT Recycling
Consumer behavior plays a crucial role in shaping the future of IT recycling. As individuals become more aware of the environmental impact of electronic waste, their purchasing decisions and disposal habits are being influenced by sustainability considerations. The increasing demand for sustainable electronics is driving manufacturers to adopt greener practices and create products that are designed with recyclability in mind.
Responsible purchasing is a key aspect of consumer behavior in IT recycling. Consumers are now more conscious of the lifespan and recyclability of electronic devices before making a purchase. They are actively seeking out brands that prioritize eco-friendly manufacturing processes, use recyclable materials, and offer take-back programs for end-of-life products. This shift in consumer behavior encourages manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices throughout the product lifecycle, from design to disposal.
Furthermore, consumer awareness and education play a vital role in promoting responsible IT recycling. As individuals learn about the environmental impact of e-waste and the benefits of recycling, they are more motivated to dispose of their old electronic devices correctly. Many countries and organizations have implemented educational campaigns to increase awareness about the importance of IT recycling, which has resulted in a positive change in consumer behavior.

Consumer Behavior and Sustainable Electronics
The adoption of sustainable electronics is a direct result of changing consumer behavior. Consumers now prioritize devices that are energy-efficient, made with recycled or sustainable materials, and have a longer lifespan. They are willing to pay more for products that align with their values and have a lower environmental impact. This shift in consumer preferences has pushed manufacturers to innovate and develop greener technologies.
By considering the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions and making conscious choices, consumers have the power to drive change in the IT recycling industry. Their demand for sustainable electronics encourages manufacturers to prioritize sustainability and invest in eco-friendly practices. Consumer behavior is a catalyst for a more responsible and sustainable future in IT recycling, paving the way for innovative solutions and technologies that minimize electronic waste and preserve valuable resources.
Regulatory Changes and Policies in IT Recycling
Regulatory changes and policies play a crucial role in shaping the future of IT recycling. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to ensure responsible e-waste management and promote a more sustainable approach to technology disposal. These regulations encompass various aspects of IT recycling, including guidelines for data destruction, material recovery, and disposal methods.
One of the key motivations behind these regulatory changes is the growing concern over the environmental impact of electronic waste. As the volume of e-waste continues to rise, governments are taking proactive measures to mitigate its harmful effects on the environment. By enforcing stricter regulations, they aim to minimize the improper disposal of electronic devices, promote the recycling of valuable resources, and reduce the pollution caused by hazardous materials found in e-waste.
“Governments are realizing the urgency of implementing sustainable e-waste management practices and are enacting legislation to ensure compliance across the industry,” said Lisa Johnson, an expert in environmental policy.
Non-compliance with these regulations can have severe consequences for companies. Fines and penalties are imposed to deter irresponsible practices and encourage businesses to adopt more sustainable IT recycling methods. This creates a sense of urgency and accountability within the industry, driving companies to prioritize responsible e-waste management and seek out eco-friendly solutions.
The Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes in IT recycling have far-reaching implications. They not only protect the environment but also foster a culture of sustainability and encourage innovation in the industry. Companies are compelled to develop new strategies and technologies that comply with these regulations, leading to the emergence of more efficient and eco-friendly IT recycling practices.
Key Policies in IT Recycling
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) | Requires manufacturers to take responsibility for their products throughout their lifecycle, including their proper disposal and recycling. |
| Data Destruction and Privacy Regulations | Guidelines for the secure erasure of data from electronic devices to protect consumer privacy and prevent data breaches. |
| Material Recovery and Recycling Targets | Specific goals set by governments to encourage the recovery and recycling of valuable materials, such as precious metals and rare earth elements, from e-waste. |
| Ban on Landfilling of E-Waste | Prohibits the disposal of electronic waste in landfills, encouraging the recycling and proper treatment of e-waste instead. |
These policies, along with others, are instrumental in driving the industry towards a more responsible and sustainable future. The combined efforts of governments, businesses, and consumers in adhering to and advocating for these regulatory changes will have a profound impact on the IT recycling landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities in IT Recycling
The future of IT recycling presents both challenges and opportunities. As technology continues to advance, ensuring data security becomes a major challenge. With electronic devices storing increasing amounts of sensitive information, it is crucial to implement robust security measures during the recycling process to protect against data breaches and privacy concerns.
Another challenge is resource scarcity. Electronic devices contain rare earth elements that are becoming increasingly scarce. Properly managing and recovering these valuable resources from e-waste is essential for reducing reliance on mining and conserving limited natural resources.
The economic viability of IT recycling programs is often questioned. Some argue that the costs associated with recycling outweigh the benefits. However, advancements in technology are making the recycling process more cost-effective and efficient. By leveraging automation, artificial intelligence, and innovative recycling techniques, the economic viability of IT recycling can be improved.
Economic Viability of IT Recycling
“Advancements in technology are making the recycling process more cost-effective and efficient.”
Despite the challenges, there are also significant opportunities in IT recycling. Technological advancements offer possibilities for enhancing recycling methods and improving overall sustainability. For example, AI can be applied to automate the sorting and categorization of e-waste, increasing efficiency and accuracy. IoT devices can enable real-time monitoring of electronic devices, helping to identify potential recycling opportunities and optimize resource recovery processes.
Public awareness and education play a vital role in driving sustainable IT recycling practices. By increasing awareness of the environmental impact of e-waste and promoting responsible recycling behavior, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable future. Additionally, businesses, governments, and educational institutions can take proactive steps to promote sustainable IT recycling by integrating responsible disposal practices, prioritizing data security, and adapting their policies and curricula to align with environmentally-friendly practices.
| Challenge | Opportunity |
|---|---|
| Data Security | Technological Advancements |
| Resource Scarcity | Economic Viability |
| Public Awareness and Education |
Actionable Steps for a Sustainable Future in IT Recycling
Creating a sustainable future in IT recycling requires the collective effort of individuals, businesses, governments, and educational institutions. By taking actionable steps, we can contribute to responsible disposal, eco-friendly purchasing, and effective e-waste management. Here are some key actions that each stakeholder can take:
Individuals:
As individuals, we can start by educating ourselves about responsible recycling practices. This includes understanding how to properly dispose of electronic devices and ensuring they are recycled through certified e-waste recycling programs. By making eco-friendly purchasing decisions, such as buying refurbished or energy-efficient devices, we can reduce electronic waste and promote a more sustainable future.
Businesses:
Businesses play a crucial role in driving sustainable IT recycling practices. They can prioritize data security by implementing robust data destruction protocols and partnering with certified recycling vendors. Providing training and awareness programs for employees on responsible e-waste disposal is essential. Adopting a circular economy approach, businesses can explore opportunities for refurbishing or reselling old devices, contributing to a more circular and sustainable IT ecosystem.
Governments:
Governments have the power to enforce stricter regulations and policies to ensure responsible e-waste management. They can implement measures that promote sustainable practices such as extended producer responsibility (EPR), which holds manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products. Governments can also run public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the importance of IT recycling and encourage them to participate in recycling programs.
Educational Institutions:
Educational institutions can play a vital role in promoting a sustainable future in IT recycling. By integrating sustainable computing and IT recycling into their curriculum, they can educate and train future generations on responsible waste management practices. Additionally, conducting research and development projects focused on improving waste management techniques and developing innovative recycling technologies can contribute to more efficient and sustainable e-waste disposal solutions.

| Stakeholder | Actionable Steps |
|---|---|
| Individuals | Educate themselves about responsible recycling practices |
| Ensure proper disposal of electronic devices | |
| Make eco-friendly purchasing decisions | |
| Businesses | Implement robust data destruction protocols |
| Partner with certified recycling vendors | |
| Explore opportunities for refurbishing or reselling old devices | |
| Governments | Enforce stricter regulations for responsible e-waste management |
| Implement measures like extended producer responsibility (EPR) | |
| Run public awareness campaigns | |
| Educational Institutions | Integrate sustainable computing and IT recycling into the curriculum |
| Conduct research and development projects for efficient waste management |
By collectively taking these actionable steps, we can contribute to a sustainable future in IT recycling. It is through the combined efforts of individuals, businesses, governments, and educational institutions that we can make a significant impact on responsible disposal, eco-friendly purchasing, and effective e-waste management.
Conclusion
The future of IT recycling is driven by technology advancements, consumer awareness, regulatory compliance, and the collective efforts of individuals, businesses, governments, and educational institutions. As technology continues to evolve, IT recycling practices become more sustainable and efficient. With increased consumer awareness and responsible behavior, the demand for sustainable electronics grows. Stricter regulations and policies ensure responsible e-waste management. By taking actionable steps towards a sustainable future, we can create a world where IT recycling plays a crucial role in preserving the environment and promoting responsible technology disposal.
FAQ
What are the emerging technologies in IT recycling?
Emerging technologies in IT recycling include artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain.
How does AI contribute to IT recycling?
AI is used to automate the sorting of e-waste, making the recycling process more efficient.
What is the role of IoT in IT recycling?
IoT is leveraged to monitor the condition of electronic devices in real-time, ensuring they are disposed of responsibly.
How does blockchain technology help in IT recycling?
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to track the lifecycle of electronic components, enhancing the transparency of IT recycling processes.
How does consumer behavior impact IT recycling?
Consumer awareness of the environmental impact of e-waste drives the demand for sustainable electronics and influences manufacturers to adopt greener practices.
What role do regulatory changes play in IT recycling?
Governments implement stricter regulations to ensure responsible e-waste management, including guidelines for data destruction, material recovery, and disposal methods.
What are the challenges in IT recycling?
Challenges in IT recycling include ensuring data security and dealing with resource scarcity, as electronic devices contain rare earth elements that are becoming scarce.
Are recycling programs economically viable?
Advancements in technology are making the recycling process more cost-effective, improving the economic viability of recycling programs.
What can individuals do to promote sustainable IT recycling?
Individuals can educate themselves about responsible recycling practices and ensure proper disposal of electronic devices.
How can businesses contribute to sustainable IT recycling?
Businesses can adopt sustainable practices, prioritize data security, and provide employee training on responsible IT recycling.
What steps can governments take to promote responsible e-waste management?
Governments can enforce stricter regulations, run public awareness campaigns, and collaborate with industry stakeholders to promote responsible e-waste management.
What initiatives can educational institutions undertake for sustainable IT recycling?
Educational institutions can integrate sustainable computing and IT recycling into their curriculum, conduct research and development for efficient waste management, and raise awareness among students.
What drives the future of IT recycling?
The future of IT recycling is driven by technology advancements, consumer awareness, regulatory compliance, and the collective efforts of individuals, businesses, governments, and educational institutions.