Understanding the Different Grades of Recycled IT Equipment
Recycling unwanted electrical and electronic equipment is essential for the environment. Lead and other toxins in these products can contaminate soil and water, causing harm to wildlife and human health. The Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Regulations in the UK ensure that these products are properly disposed of and recycled. There are different grades of recycled IT equipment, each with its own distinctions and uses.
Key Takeaways:
- Recycling IT equipment helps protect the environment and reduce health risks.
- The WEEE Regulations in the UK govern the proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste.
- There are different grades of recycled IT equipment based on appearance and condition.
- Understanding these grades is important for businesses and individuals looking to recycle their old devices.
- Proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste contribute to a more sustainable future.
Benefits of Recycling IT Equipment
Recycling unwanted electrical and electronic equipment offers numerous environmental benefits. By recycling IT equipment, we can conserve natural resources and significantly reduce the environmental and health risks associated with improper disposal. When electronic waste is sent to landfills, hazardous toxins such as lead and mercury can contaminate the soil and water, posing a threat to wildlife and human health. Recycling IT equipment helps prevent this contamination by minimizing the release of harmful substances into the environment.
Furthermore, the recycling process for IT equipment can vary depending on the specific category of the equipment and the technology used. This ensures that different components, such as metals, plastics, and circuitry, are properly extracted and processed. By recycling these valuable materials, we reduce the need for new raw materials, thus conserving energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with the extraction and production of virgin resources.
Overall, recycling IT equipment not only helps protect the environment but also promotes sustainable resource management. By embracing responsible recycling practices, we can actively contribute to a healthier and more sustainable future.
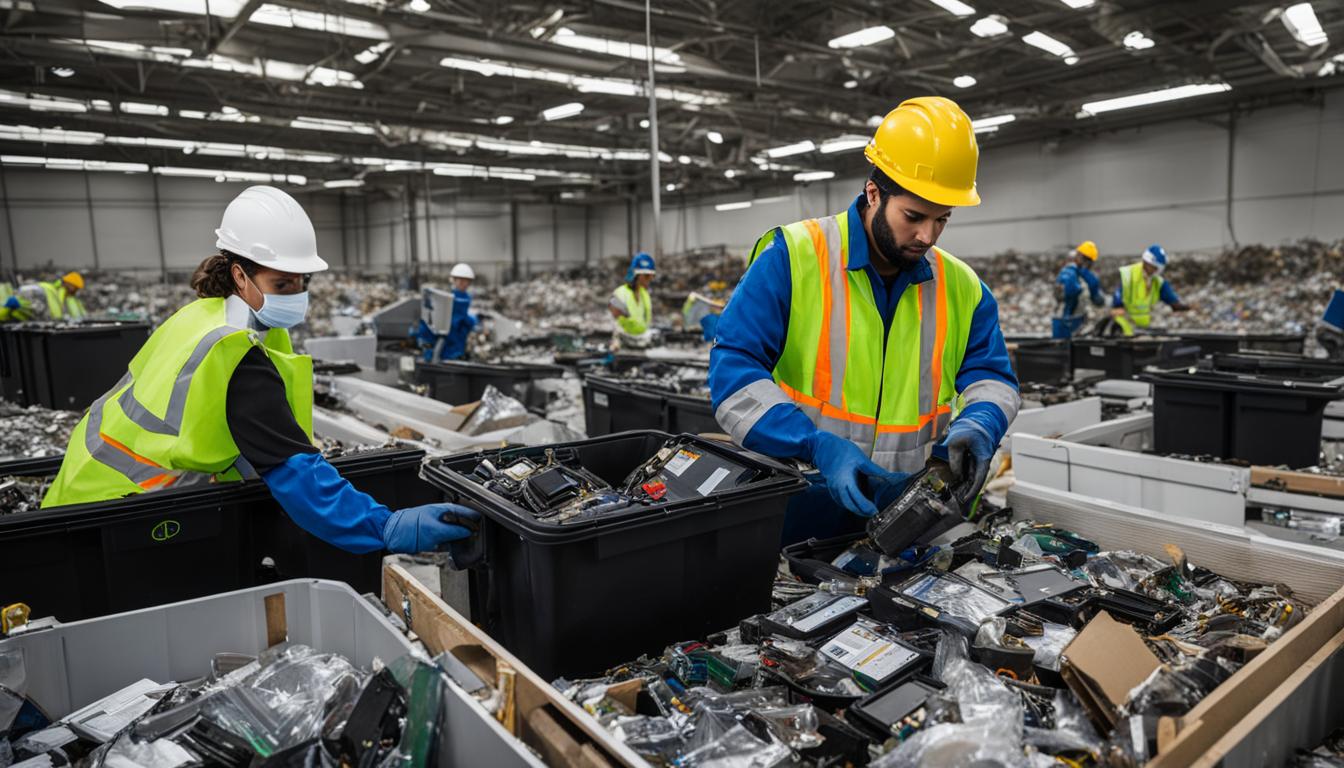
Disposal and Treatment of WEEE
The disposal and treatment of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) are regulated by the WEEE Regulations in the UK. These regulations ensure that electronic waste is handled responsibly to minimize its environmental impact and protect human health. WEEE encompasses a wide range of electrical and electronic devices, including IT equipment, TVs, small household appliances, and more.
The treatment of WEEE involves various processes aimed at recovering valuable materials and reducing the volume of waste that ends up in landfills. One common method is shredding, which breaks down the electronic waste into smaller pieces. These shredded materials can then be sorted and further processed to extract recyclable components such as metals, plastics, and glass.
Another treatment method is disassembly, where electronic devices are taken apart to separate their different components and materials. This process allows for the recovery of valuable parts and ensures that hazardous substances, such as lead and mercury, are properly handled and disposed of.
Recycling companies play a crucial role in the disposal and treatment of WEEE. They offer collection services for electronic waste, often on a like-for-like basis, meaning they collect old appliances when delivering new ones. This helps ensure that electronic devices are disposed of correctly and that valuable materials are recovered and reused, reducing the demand for new raw materials.
Table: Disposal and Treatment Methods for WEEE
| Treatment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Shredding | Electronic waste is broken down into smaller pieces through shredding processes. The shredded materials are then sorted and processed for further recycling. |
| Disassembly | Electronic devices are taken apart to separate different components and materials. This allows for the recovery of valuable parts and ensures proper handling of hazardous substances. |
| Material Recovery | Recoverable materials such as metals, plastics, and glass are extracted from electronic waste and processed for recycling. |
| Hazardous Substance Disposal | Hazardous substances found in electronic devices, such as lead and mercury, are handled and disposed of in environmentally friendly ways to prevent contamination. |
By adhering to the WEEE Regulations and working with reputable recycling providers, individuals and businesses can ensure that their electronic waste is properly disposed of and recycled, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Understanding Different Grades of Recycled IT Equipment
When it comes to recycling IT equipment, there are different grades used to classify the condition and value of the equipment. Understanding these grades is crucial for businesses and individuals looking to recycle their old electronic devices responsibly. The grades range from high-paying Grade 1 equipment to functional Grade 3 equipment.
Grade 1 equipment:
This is the highest grade of recycled IT equipment. Grade 1 equipment is clean, unalloyed, and uncoated, making it the most valuable and sought-after grade in the recycling market. Recycling companies pay top prices for Grade 1 equipment due to its pristine condition and minimal refurbishment required.
Grade 2 equipment:
Grade 2 equipment may have a slightly dirty appearance and may still have solder or coating on it. While it may not be as valuable as Grade 1, it still holds significant worth in the recycling market. Grade 2 equipment often undergoes some refurbishment before being resold or repurposed.
Grade 3 equipment:
Grade 3 equipment may have cosmetic damage or corrosion, but it is still functional. While it may not have the same value as Grade 1 or Grade 2 equipment, Grade 3 equipment can still be recycled and reused. This grade is often a more affordable option for individuals and businesses looking for second-hand IT equipment.
By understanding the different grades of recycled IT equipment, you can make informed decisions about how to recycle and dispose of your old electronic devices. Whether you have Grade 1 equipment that can fetch a higher price in the market or Grade 3 equipment that still has functional value, recycling helps protect the environment and reduces the need for new raw materials.
Copper Grades in Recycled IT Equipment
Copper is a valuable metal that can be found in various types of IT equipment. When it comes to recycling these devices, understanding the different grades of copper is essential. The copper grades in recycled IT equipment can vary, and each grade has its own value and purpose. Let’s take a closer look at the different copper grades commonly found in IT equipment recycling:
Table: Copper Recycling Grades
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| #1 Copper | This is the highest grade of copper found in IT equipment. It consists of clean, unalloyed, and uncoated copper wire or cable. #1 copper is considered the most valuable grade. |
| #2 Copper | #2 copper is a slightly lower grade compared to #1. It may have a slightly dirty appearance and can still contain solder or coating. Despite being a lower grade, it still holds value in the recycling market. |
| #3 Copper | #3 copper is a lower-grade copper that may contain cosmetic damage or corrosion. However, it is still functional and can be recycled. While it may have a lower value compared to #1 and #2 copper, it is an important resource to recover. |
When recycling IT equipment, it is crucial to properly identify and separate the different copper grades. This ensures that the copper can be efficiently processed and recycled for further use. Additionally, recycling copper not only helps conserve valuable resources but also reduces the environmental impact associated with mining and manufacturing new copper.
By understanding the different copper grades in recycled IT equipment, both individuals and businesses can make informed decisions when it comes to recycling their old electronic devices. Recycling not only benefits the environment but also contributes to the circular economy by recovering valuable materials and reducing the need for raw resource extraction. Together, let’s embrace responsible recycling practices and create a more sustainable future.

Why Recycle Electronics?
Recycling electronics is of utmost importance in today’s world. The environmental impact of electronic waste can be devastating if not managed properly. E-waste contains hazardous substances such as arsenic, lead, and mercury, which can contaminate soil, water, and air, posing serious threats to wildlife and human health. By recycling electronics, we can limit the hazards associated with these substances and protect our environment.
But the importance of recycling electronics goes beyond environmental preservation. Data protection is a crucial aspect of electronic recycling. When disposing of electronic devices, it is crucial to ensure that confidential data is securely removed. Recycling companies understand the significance of data security and employ measures to safely delete sensitive information before recycling the devices.
Moreover, recycling electronics allows for the recovery of valuable metals and other materials. In every electronic device, there are precious resources, such as gold, silver, and copper, which can be extracted and reused. By recycling electronics, we reduce the need for new raw materials, conserve natural resources, and minimize energy consumption, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Overall, recycling electronics is not only necessary to protect the environment and human health but also to promote resource conservation and data security. It is crucial for individuals and businesses to understand the importance of proper disposal and recycling methods to ensure a greener and more sustainable world.
Regulations for Recycling Electronics
Recycling electronic waste is of utmost importance for minimizing the environmental impact of discarded electricals. The Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) regulations provide a framework for the proper disposal and recycling of electronic devices. These regulations encompass a wide range of products, including those with a plug or battery, and outline specific recycling protocols for each category of electricals.
Adhering to the WEEE regulations is crucial to ensure responsible recycling practices. By following these guidelines, businesses and individuals can contribute to reducing the amount of electronic waste ending up in landfills and minimize the release of harmful substances into the environment.
Working with specialized recycling providers is essential for complying with the necessary legislation. These providers have the expertise to carry out responsible disposal processes and ensure that electronic waste is handled in accordance with the WEEE regulations. By partnering with reputable recycling companies, businesses can be confident that their electronic devices are recycled in an environmentally friendly and sustainable manner.
| Regulation | Objective |
|---|---|
| WEEE Directive | Promote the collection, treatment, and recovery of electrical and electronic waste |
| RoHS Directive | Restrict the use of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment |
| EU Battery Directive | Promote the collection and recycling of batteries and accumulators |
| Data Protection Regulations | Ensure the secure removal of confidential data from electronic devices before recycling |
Compliance with these regulations not only ensures legal compliance but also contributes to a more sustainable future by reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste. By recycling electronics responsibly, businesses and individuals can play their part in conserving resources, minimizing pollution, and protecting human health.

Conclusion
Understanding the different grades of recycled IT equipment is crucial for businesses and individuals looking to responsibly dispose of their old electronic devices. Recycling IT equipment not only benefits the environment but also reduces the health risks associated with hazardous substances. By adhering to the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) regulations and working with reputable recycling providers, we can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Recycling IT equipment offers numerous benefits. It helps save natural resources and minimizes the environmental and health hazards posed by landfilling electronic waste. Additionally, proper disposal and recycling of electronic devices prevent the release of harmful toxins into the environment, safeguarding wildlife and human health.
Furthermore, recycling IT equipment allows for the recovery of valuable materials, reducing the need for new raw resources. By recycling old devices, we can ensure that precious metals and components are reused in the production of new equipment, promoting a circular economy and reducing our carbon footprint.
In conclusion, it is of utmost importance to properly dispose of and recycle IT equipment. By understanding the different grades of recycled IT equipment, we can make informed decisions when recycling our electronic devices. Let us join hands, follow the regulations, and work with trusted recycling providers to create a sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
FAQ
What are the different grades of recycled IT equipment?
The different grades of recycled IT equipment include Grade 1, Grade 2, and Grade 3. Grade 1 equipment is clean, unalloyed, and uncoated, making it the most valuable. Grade 2 equipment may have a slightly dirty appearance and may still have solder or coating on it. Grade 3 equipment may have cosmetic damage or corrosion, but it is still functional.
What are the benefits of recycling IT equipment?
Recycling IT equipment helps save natural resources, reduces environmental and health risks, and prevents soil and water contamination. It also helps to limit the hazards associated with hazardous substances found in electronic products and provides data protection by safely removing confidential data from devices before recycling them.
How is Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) disposed of and treated?
The disposal and treatment of WEEE are regulated by the WEEE Regulations in the UK. Large household appliances, IT equipment, TVs, small household appliances, and other electronic devices make up a significant portion of WEEE. The treatment of WEEE can involve shredding technologies or disassembly processes. Recycling companies offer collection services for like-for-like basis, where they collect old appliances when delivering new ones.
What determines the grade of recycled IT equipment?
The condition of the equipment determines its grade. Grade 1 equipment is clean, unalloyed, and uncoated, while Grade 2 equipment may have a slightly dirty appearance and solder or coating on it. Grade 3 equipment may have cosmetic damage or corrosion, but it is still functional.
What are the different copper grades in recycled IT equipment?
Copper grades in recycled IT equipment include #1 copper and #2 copper. #1 copper is the most valuable grade and includes clean, unalloyed, and uncoated copper wire or cable. #2 copper is a slightly lower grade and may have a dirty appearance and solder or coating on it.
Why is recycling electronics important?
Recycling electronics is important to limit the hazards associated with hazardous substances found in electronic products, prevent environmental contamination, and recover valuable metals. It also contributes to data protection by safely removing confidential information from devices before recycling.
What are the regulations for recycling electronics?
Recycling electronic waste is regulated by the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) regulations. These regulations cover a wide range of products that have a plug or battery and outline recycling protocols for different categories of electricals. Adhering to these regulations ensures proper disposal and minimizes environmental impact.
What is the conclusion about the different grades of recycled IT equipment?
Understanding the different grades of recycled IT equipment is essential for businesses and individuals looking to recycle their old electronic devices. Recycling IT equipment not only helps protect the environment but also reduces the health risks associated with hazardous substances. It ensures that valuable materials are recovered and used in the production of new devices. By following the regulations and working with reputable recycling providers, we can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.